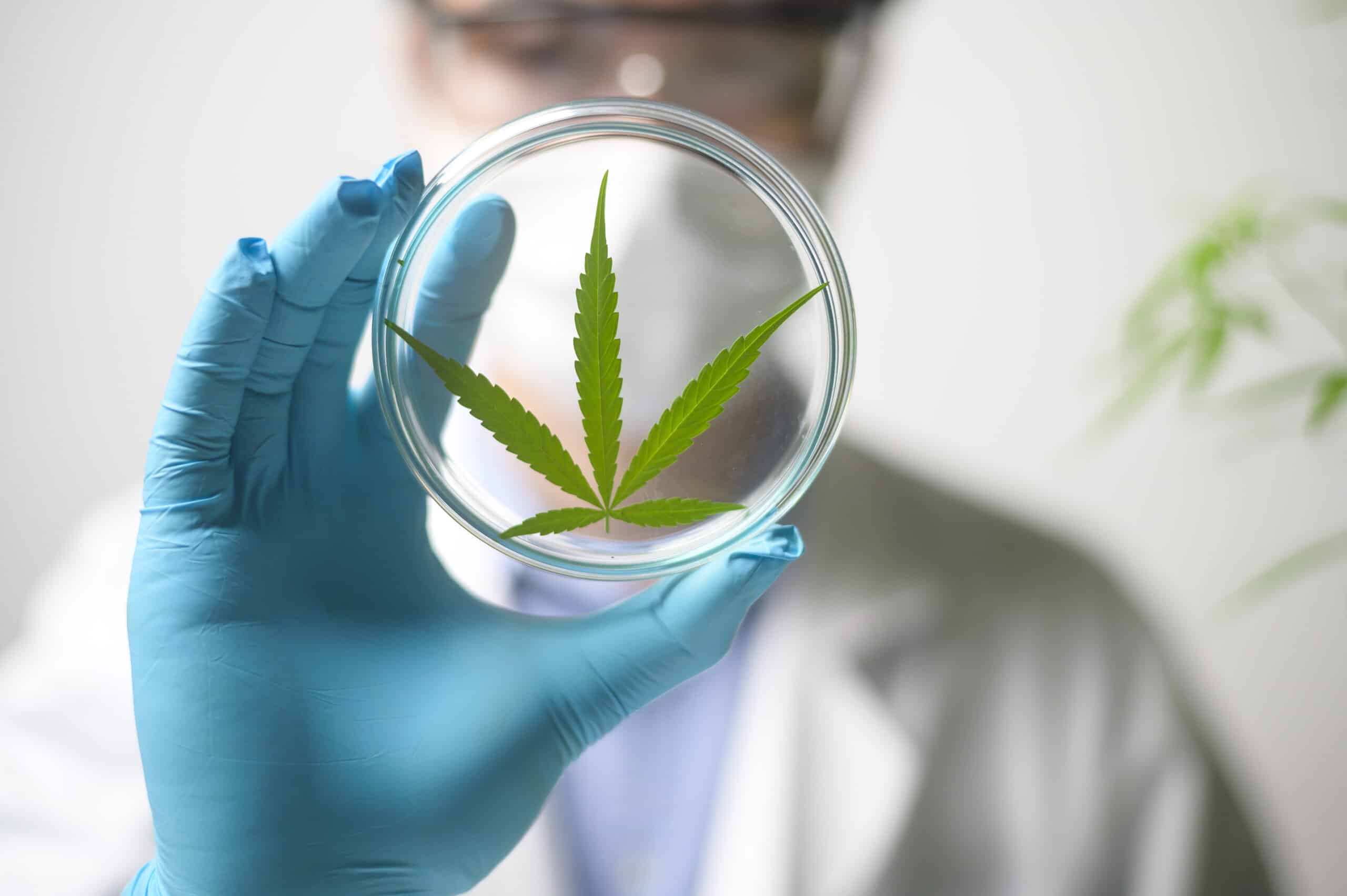
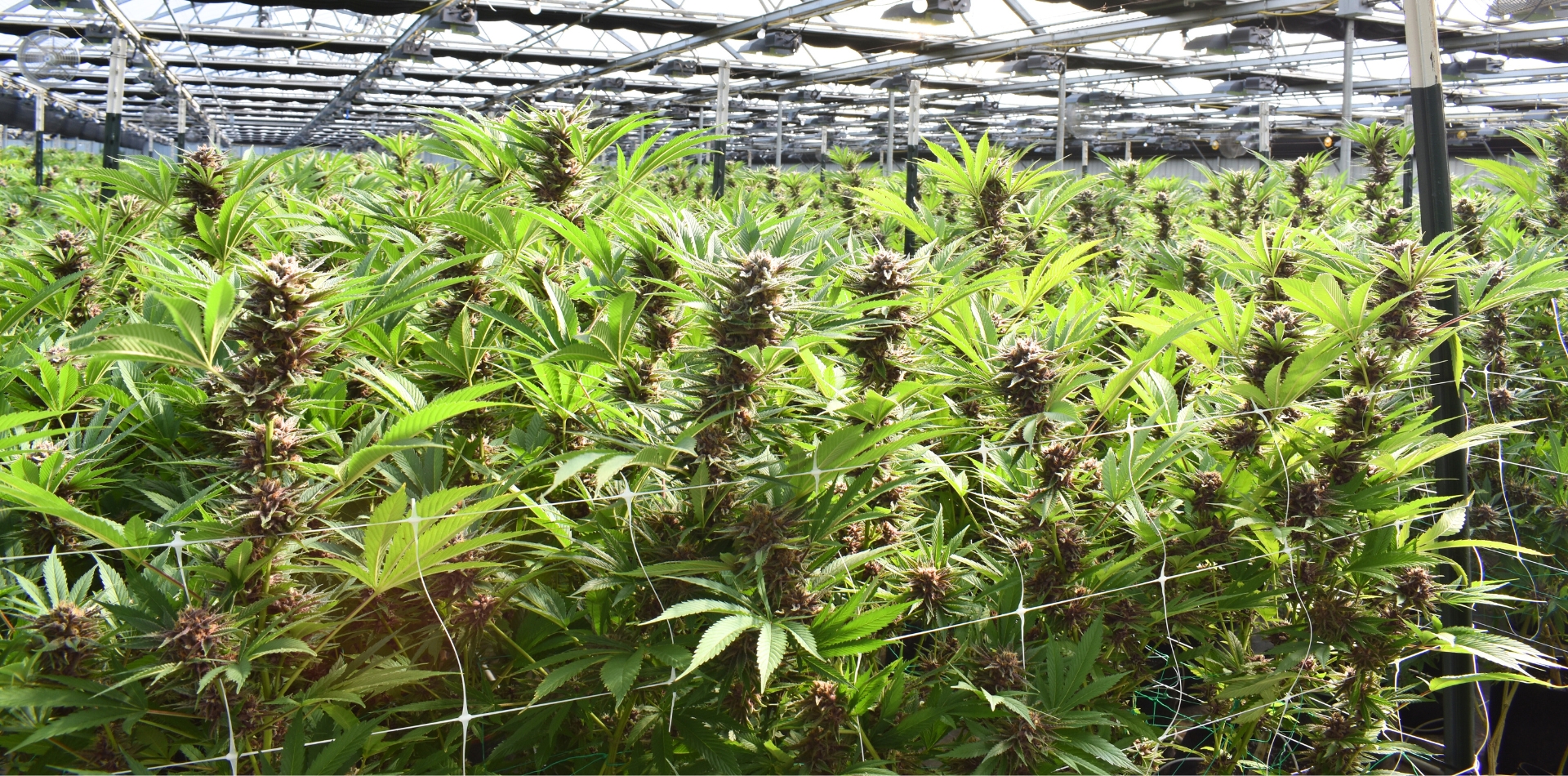
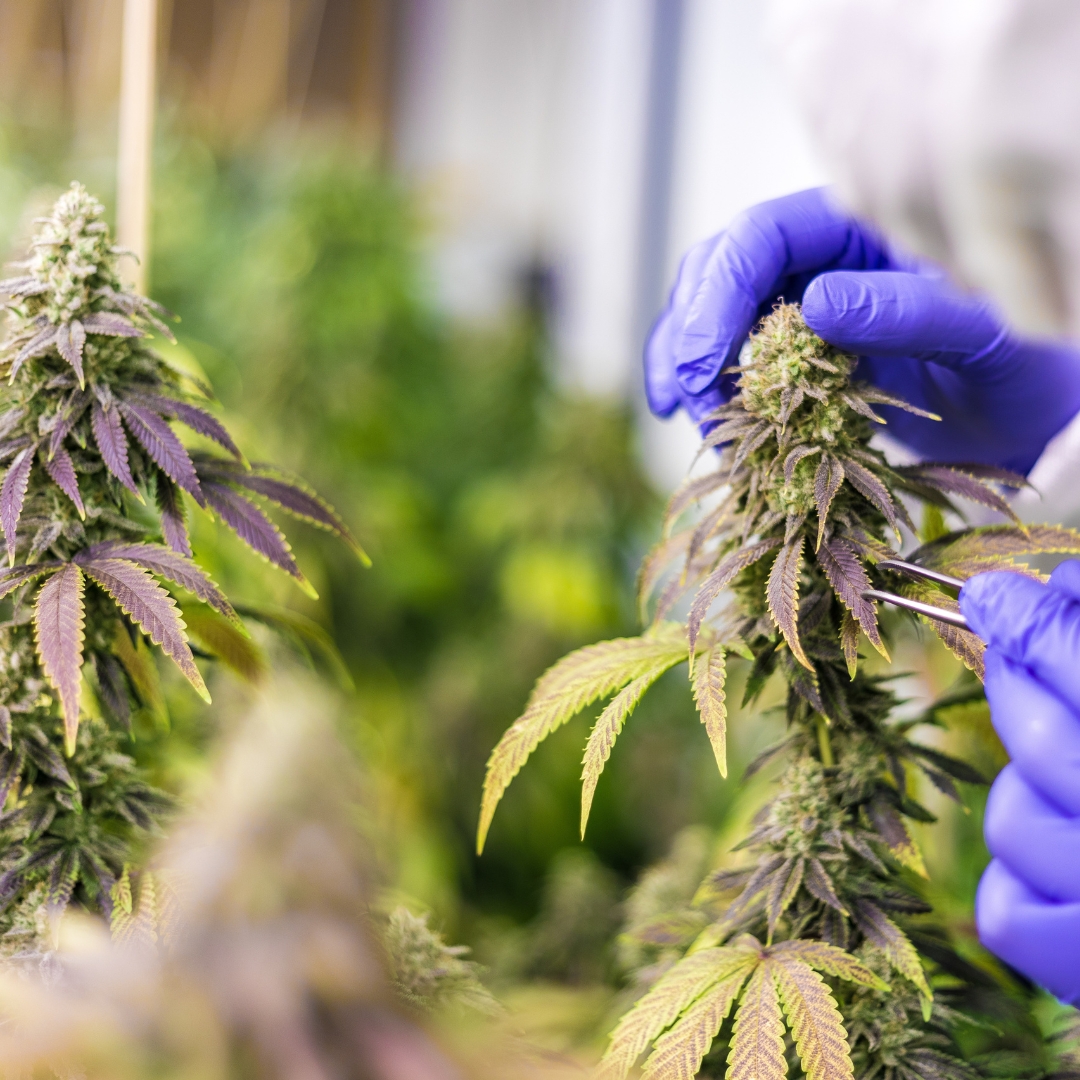
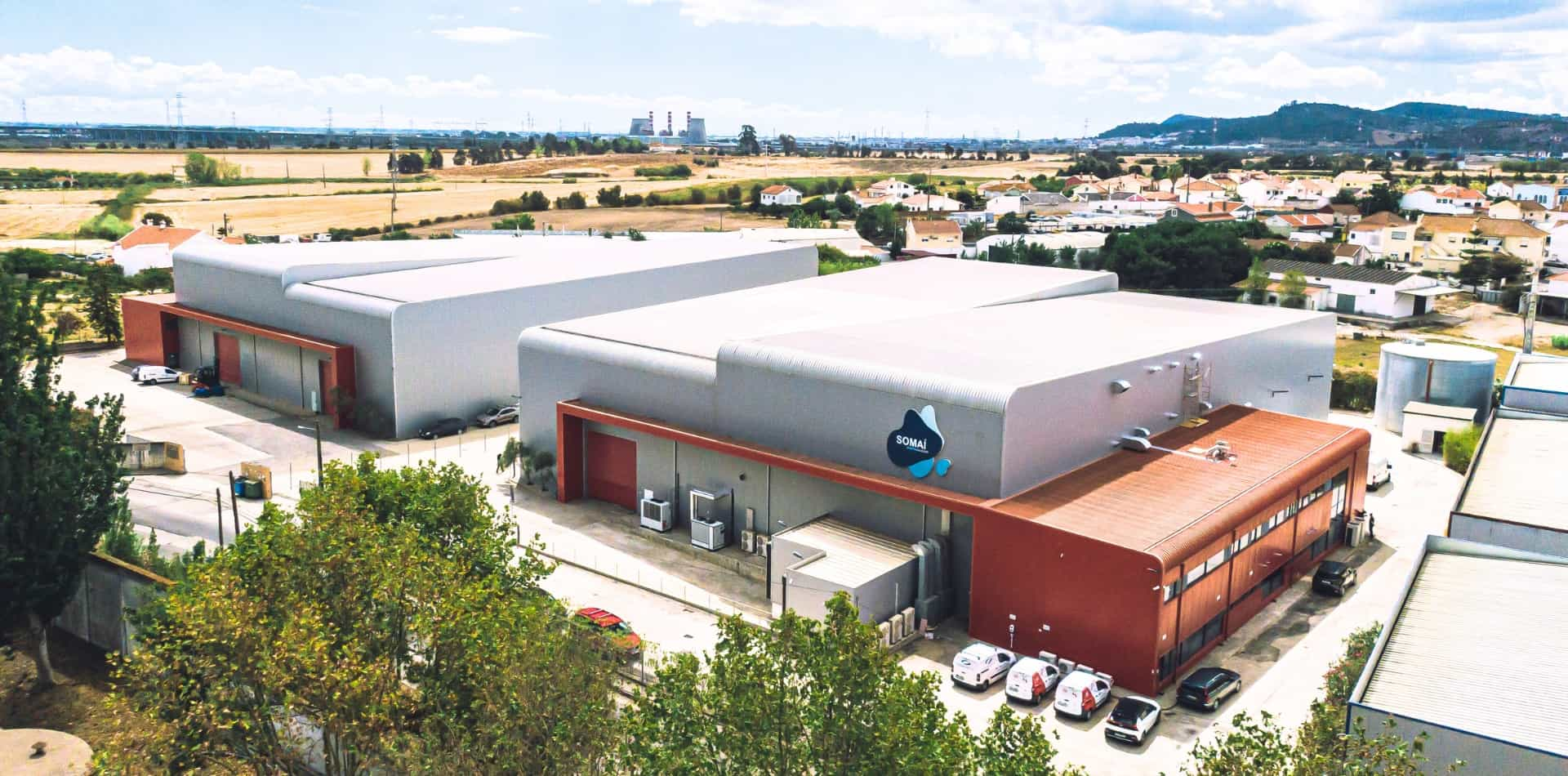
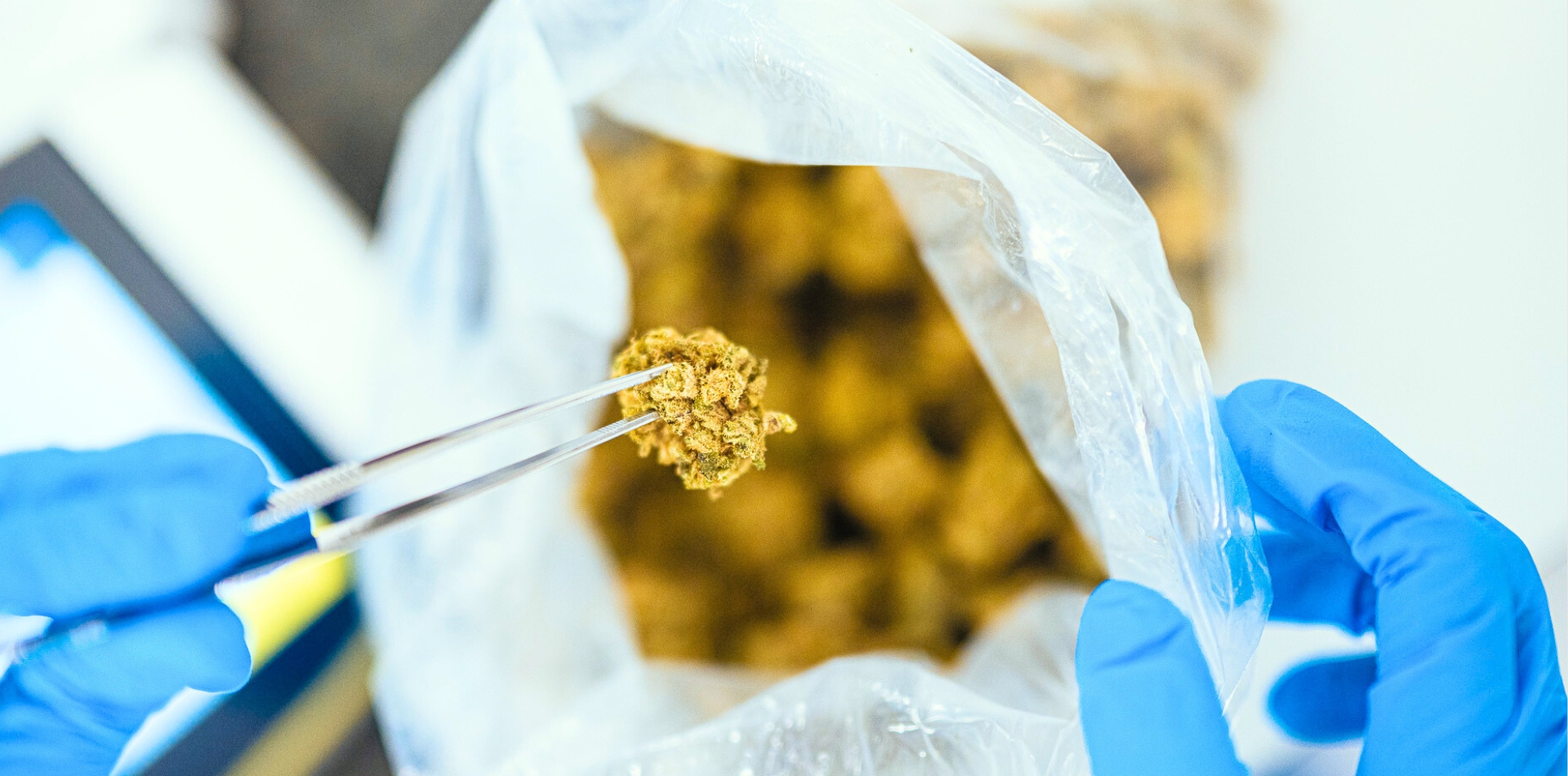
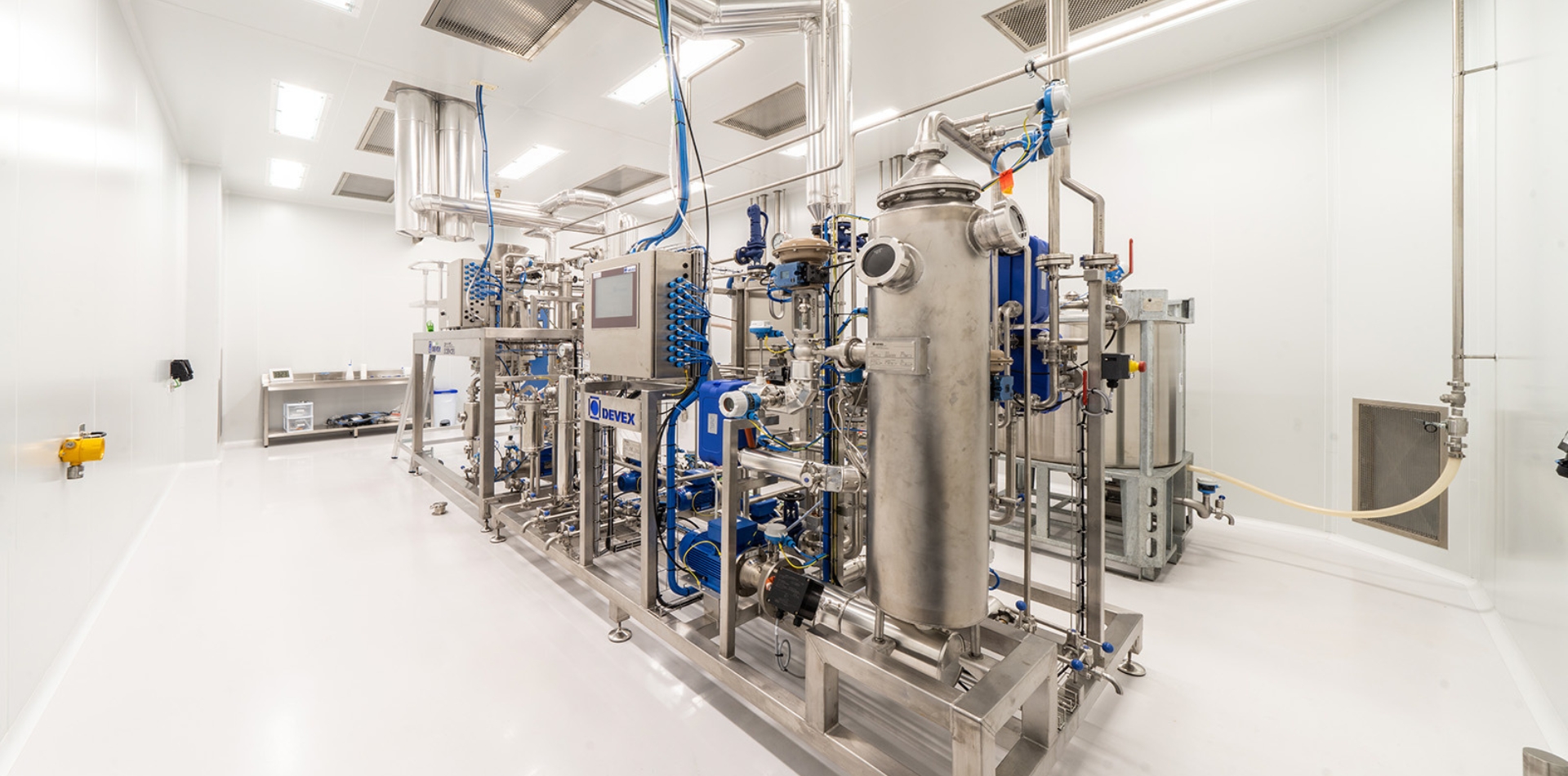
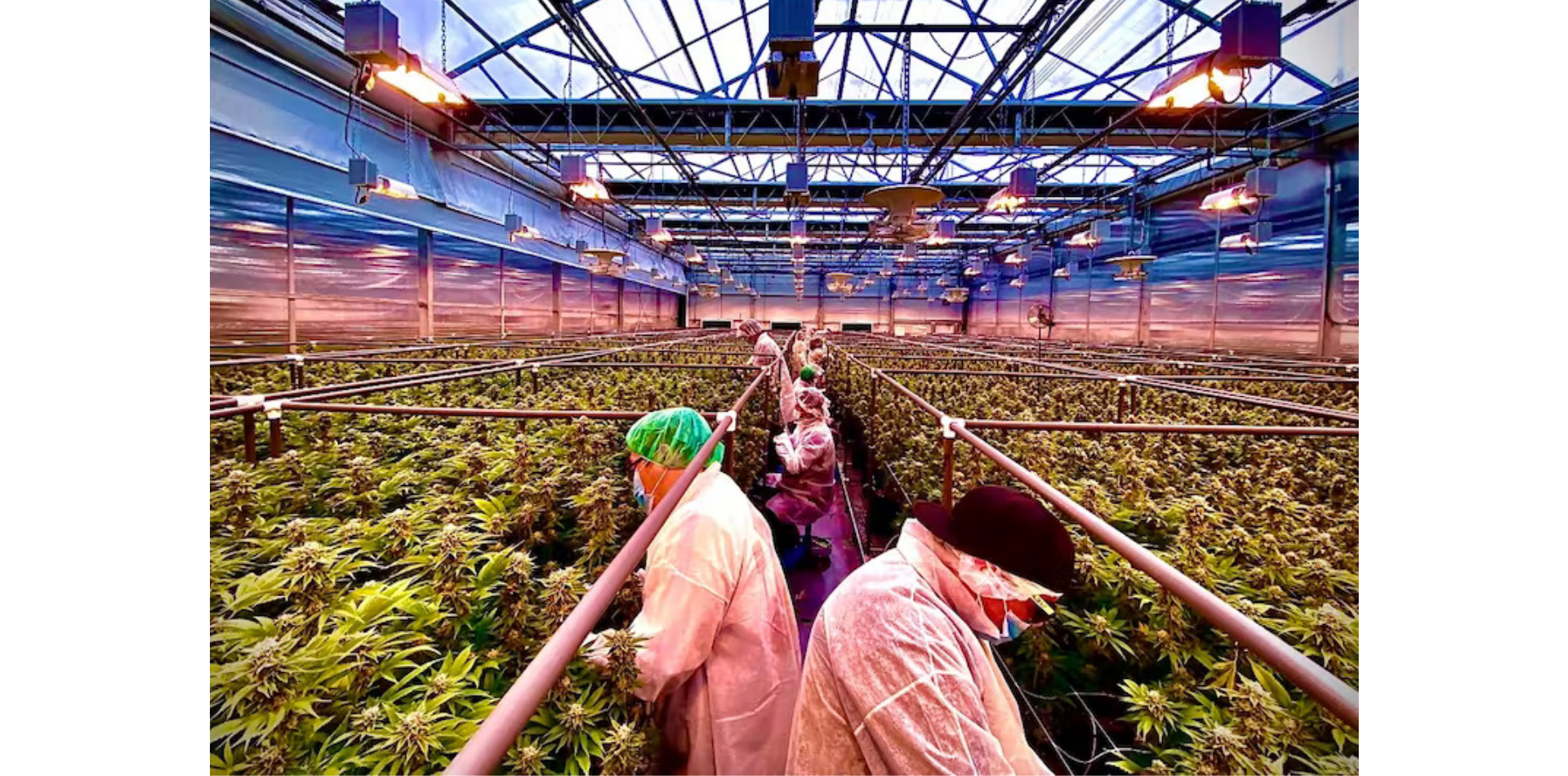
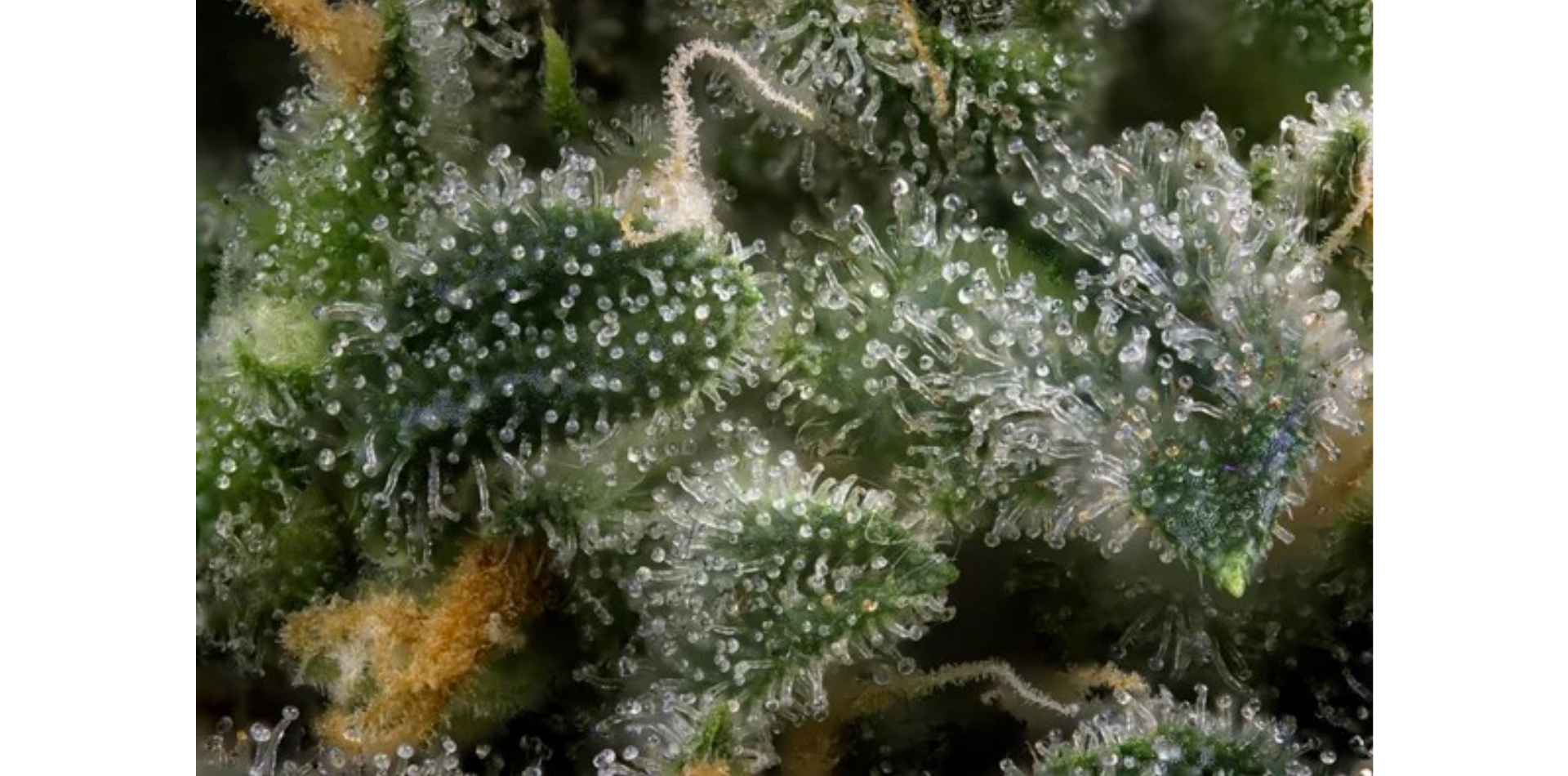
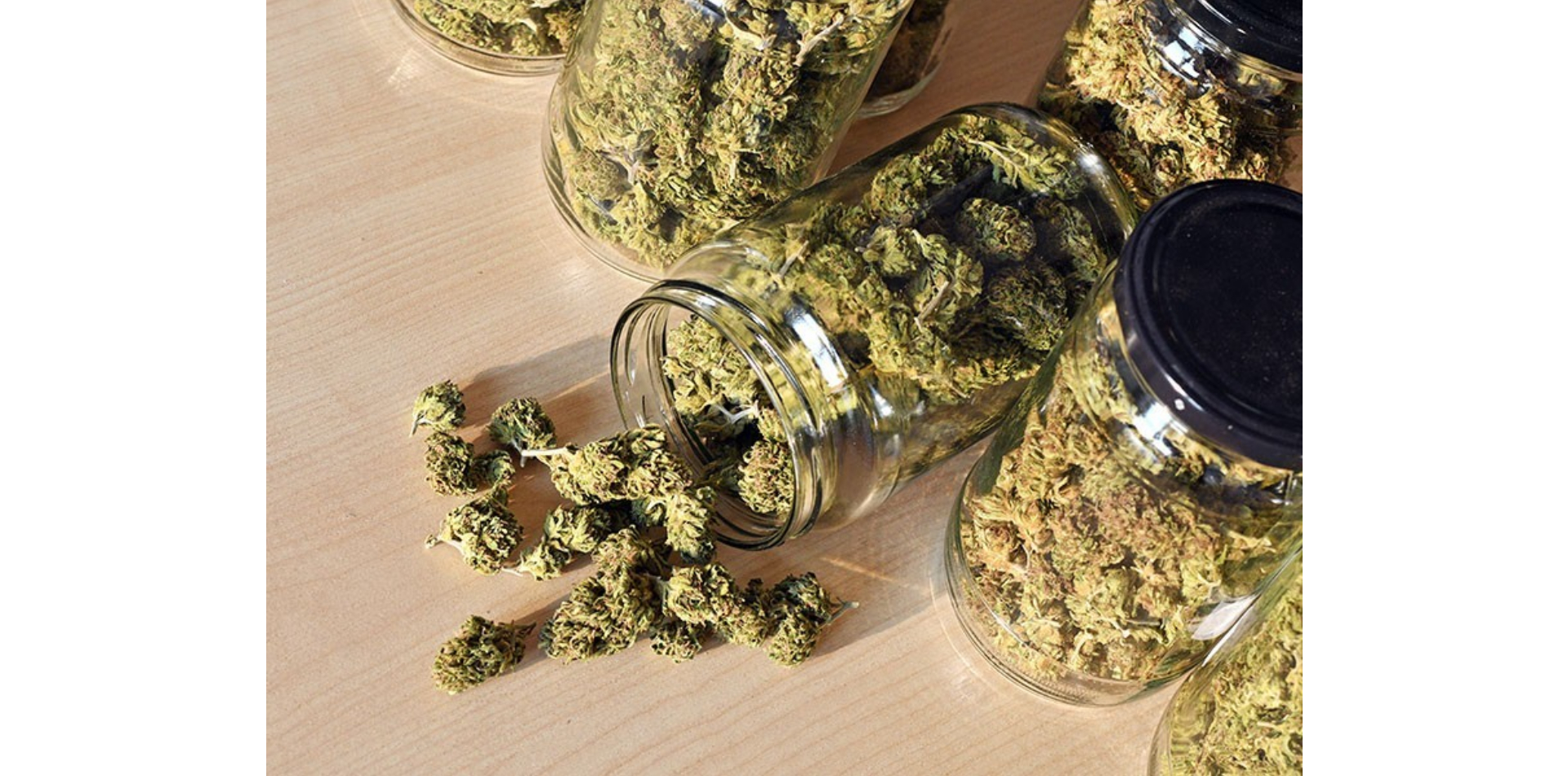
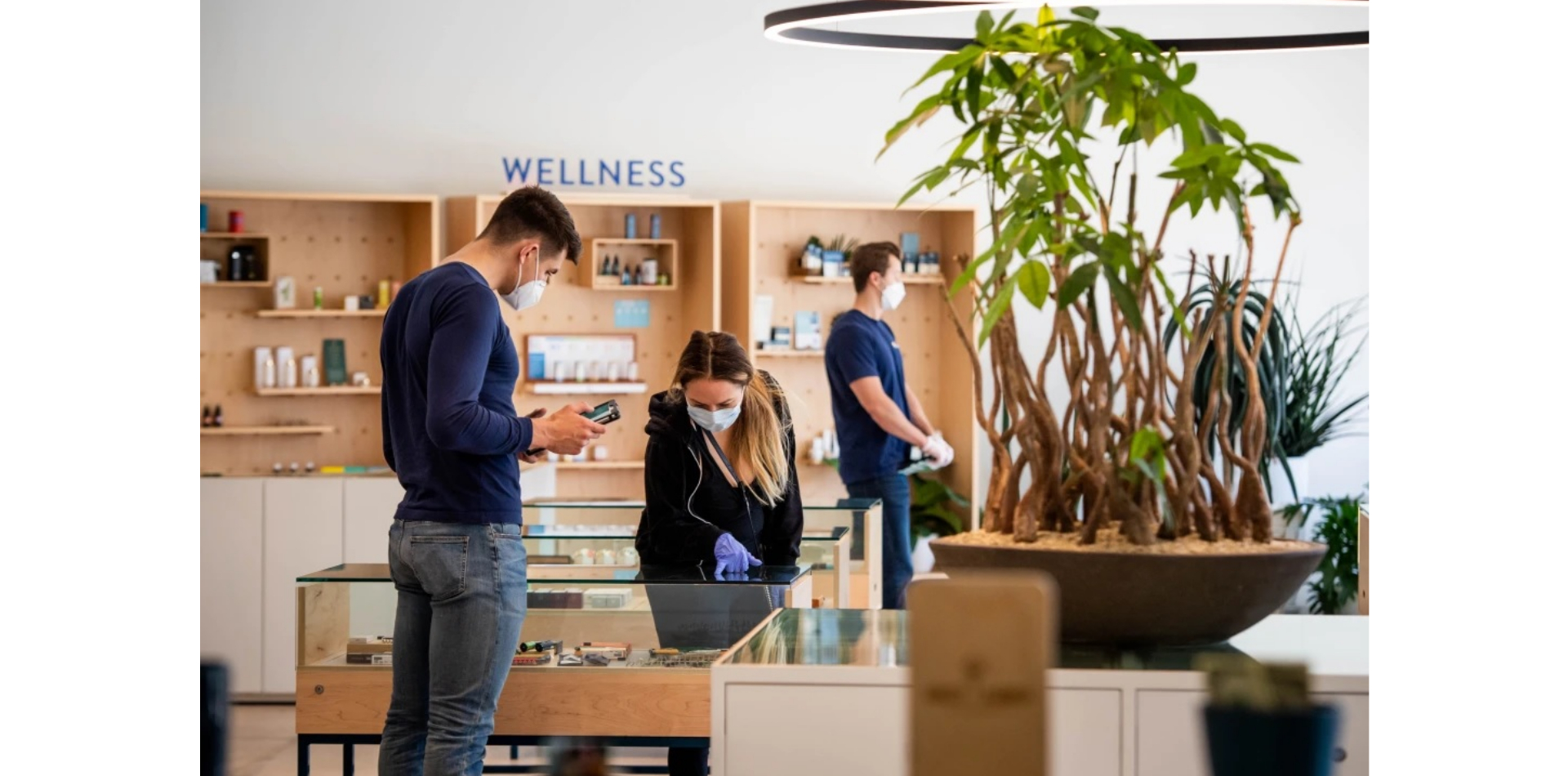
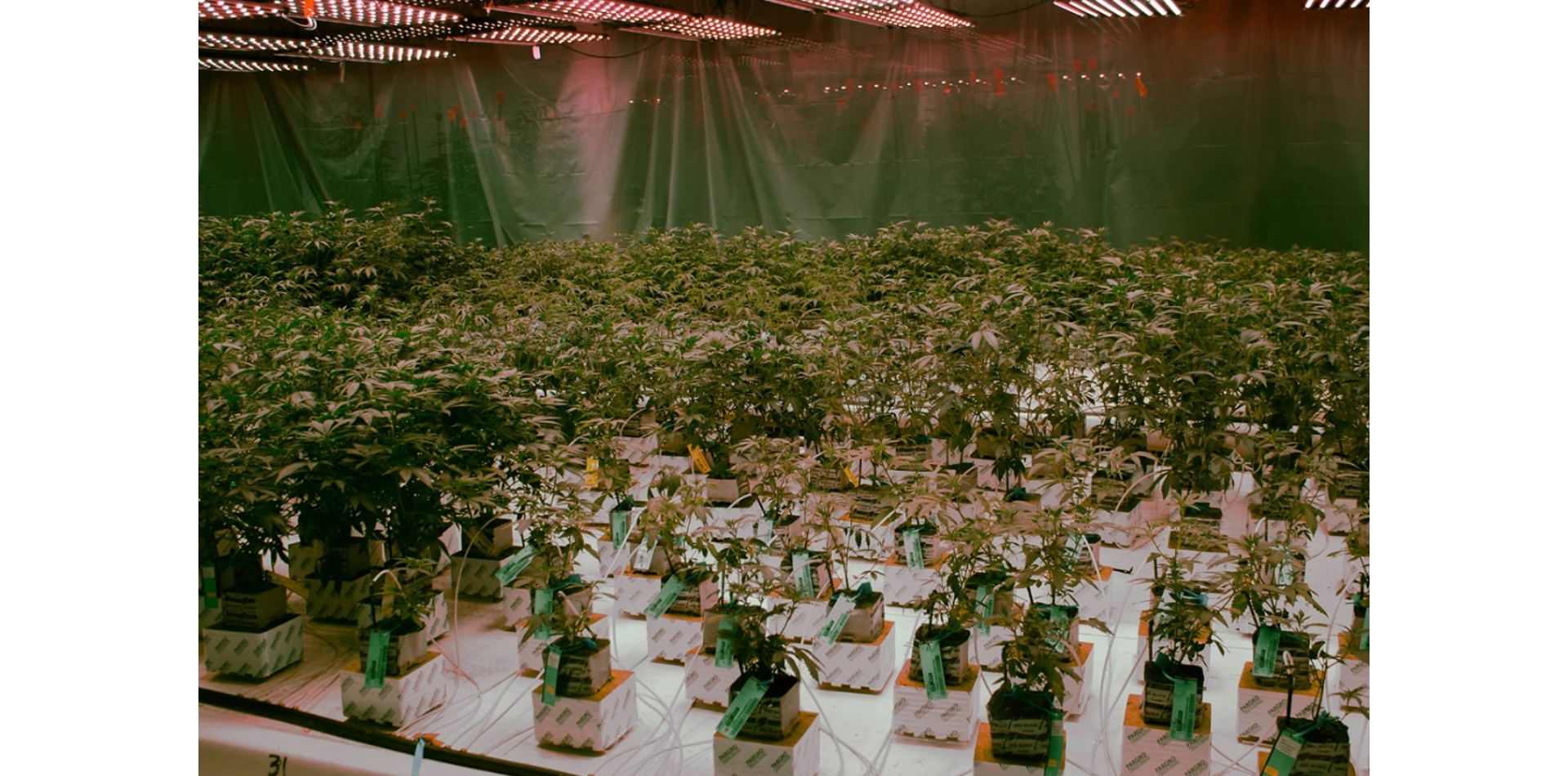
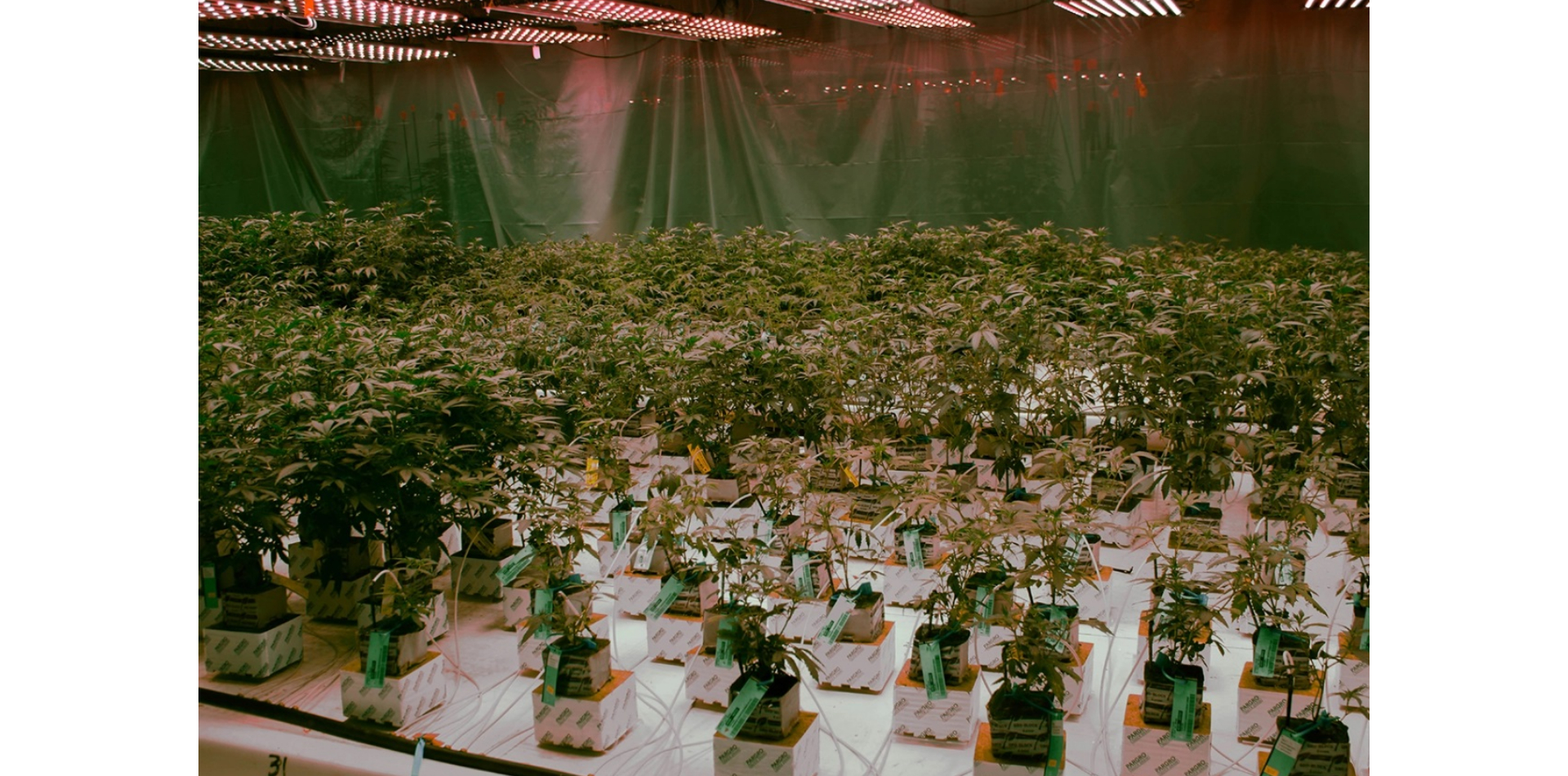
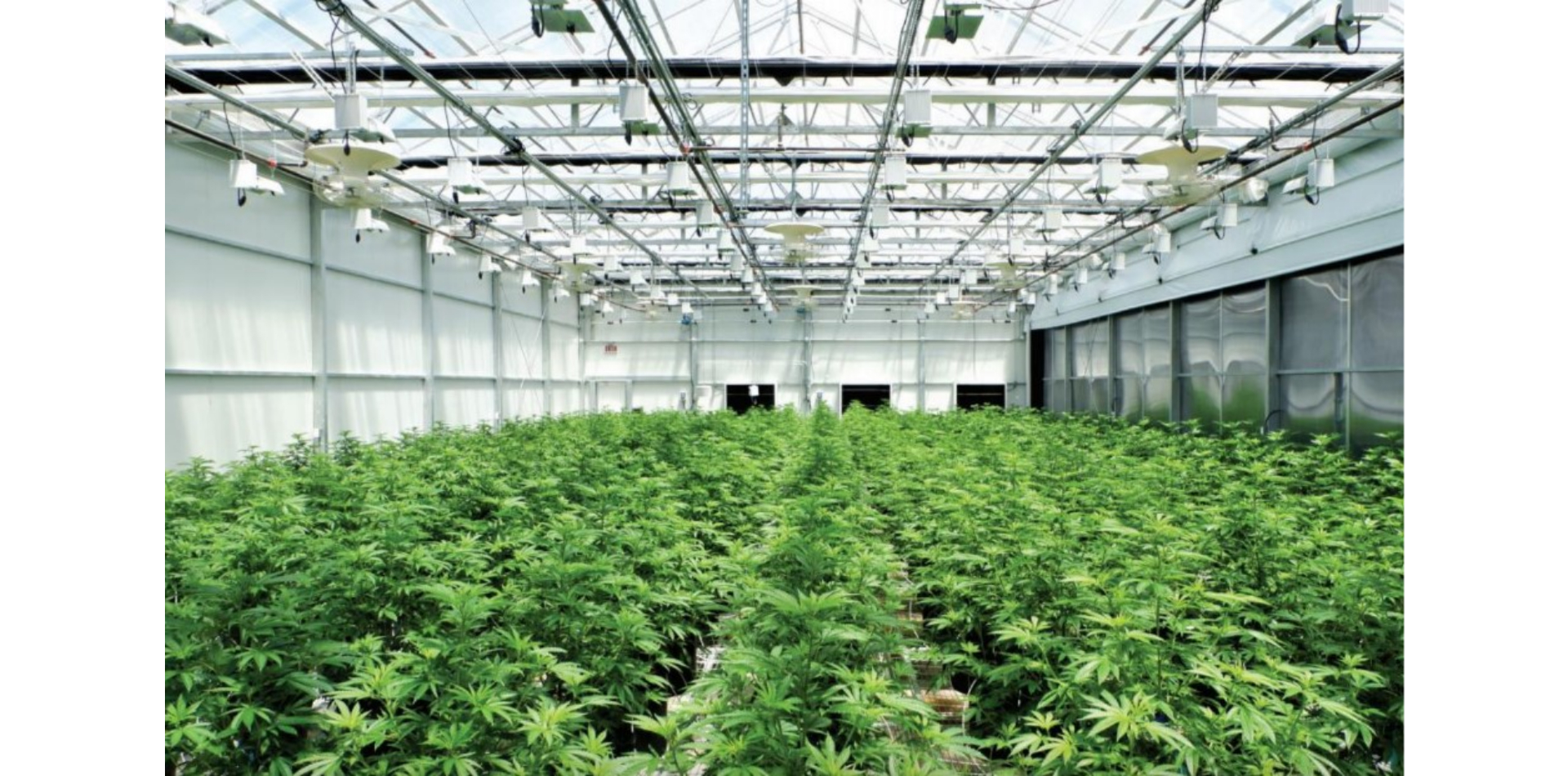
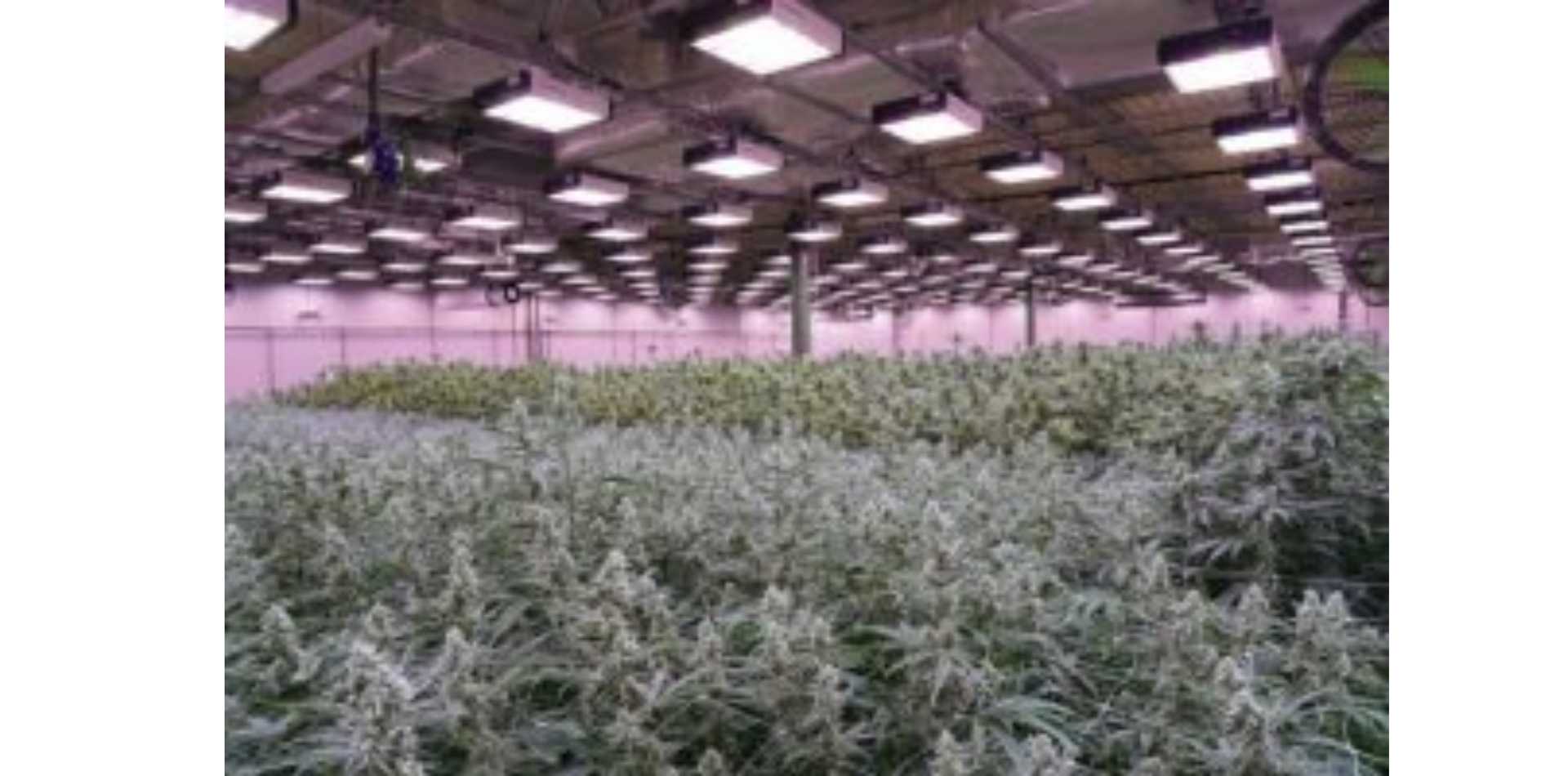
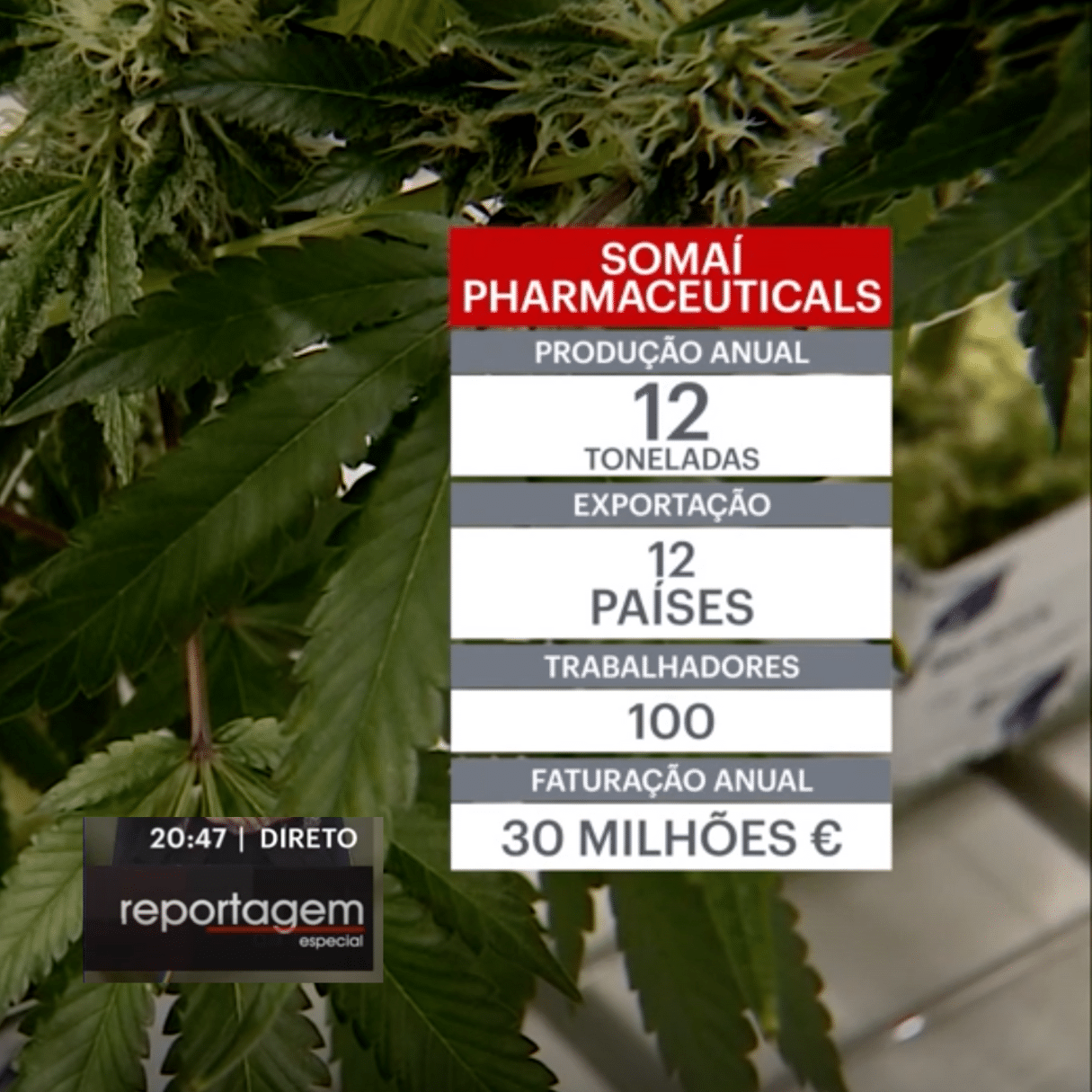
SOMAÍ and Lusófona University Publish Peer-Reviewed Study Showcasing Best Practices in Full-Spectrum Cannabis Oil Production
Lisbon, Portugal — [1 July 2025] — SOMAÍ, a leading EU-GMP-certified vertically integrated Multi-Country Operator (MCO) specializing in cannabinoid-based medicines,...
SOMAÍ Partners with Cookies Creative Consulting & Promotions, Inc. to Launch Berner’s Signature Series in Australia
We’re proud to announce a major milestone: SOMAÍ is partnering with Cookies Creative Consulting & Promotions, Inc. of California (Cookies...
VCA Deutschland Podcast. FOLGE 66 – Michael Sassano: Ein kritischer Blick
Heute spreche ich mit Michael Sassano. Er ist kein Patient, sondern der CEO der Firma SOMAÍ, die in Portugal unter...
“Portugal está a estabelecer-se como um centro de cultivo e produção de canábis medicinal na Europa” – Michael Sassano, SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
A SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals atua na distribuição de preparações e substâncias à base da canábis medicinal. Em Portugal, tem toda a...
Precision Over Potency: Personalised Cannabis Medicine is Coming of Age
One of the key differences between medical cannabis and other more traditional treatments is the highly personalised nature of how...
Thailand: The Cannabis Capital of Asia and Beyond
Thailand is already the largest global medical cannabis market, with $1.2 billion in local sales. But that’s not all — Thailand...
Herer Legacy Goes Global: Dan Herer and Somai Pharmaceuticals Bring the Jack Herer Standard to the World
Dan Herer, son of the legendary Jack Herer, partners with Somai Pharmaceuticals to take the Herer standard worldwide. Blending grassroots...
How To Trade Cannabis Flower Globally: A Story Of Capital
The global medical cannabis markets are growing faster than we could have predicted, and new countries are expected to come...
Michael Sassano Talks Global Cannabis Markets, Regulatory Challenges, and Somai’s Vision from Sydney to Lisbon
Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals, discusses global cannabis expansion, navigating regulations, and the future of cannabis products. Discover how...
Jack Herer Enters Global Pharma Market Through Partnership with SOMAÍ
The Jack Herer Brand, an iconic U.S.-based cannabis company, has announced a strategic partnership with SOMAÍ, a leading EU-GMP-certified vertically...
SOMAÍ Partners with SHERBINSKIS and BOUTIQ
A New Era for Medical Cannabis: SOMAÍ Teams Up with Iconic California Brands SHERBINSKIS and BOUTIQ for Europe and Australia...
Ireland Could Make Great Cannabis Policy: Examining the Past to Look Forward
Access to safe and controlled cannabis for the Irish people is being decided upon in 2025. Watching a country make...
Product Dumping, White Labels, and Conflicts of Interest Lead to Global Cannabis Price Catastrophe
2025 has kicked off fast and furious for the global cannabis industry as volumes increase and more countries come online...
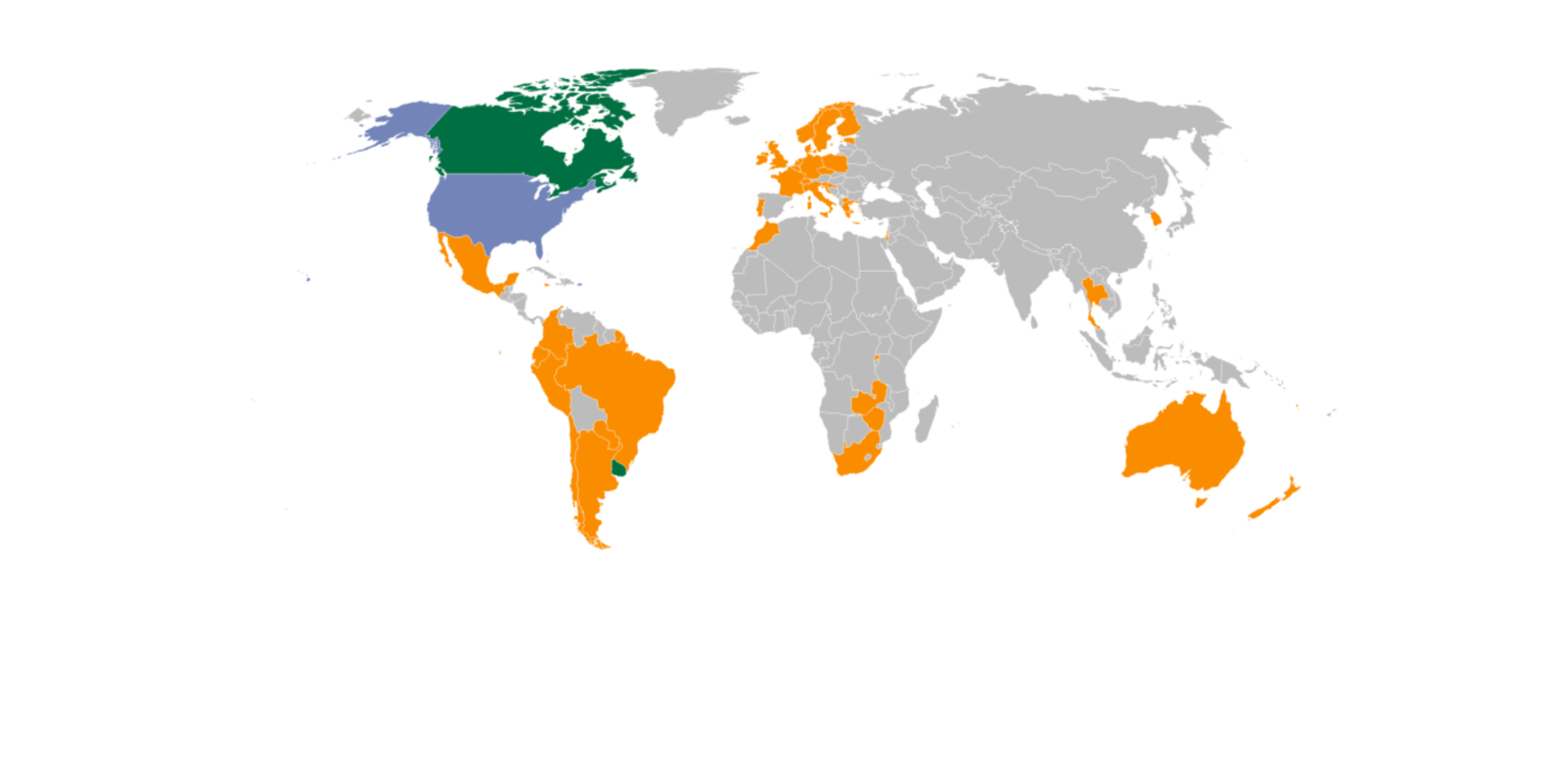
The Rise of Multi-Country Operators: Somai Targets 20 Countries by Year End
Multi-state operators, or MSO’s, have long represented the biggest and most influential cannabis players in North America. Yet, as that...
The Shift Toward Recognised Brands in Medical Cannabis
For years, medical cannabis has been treated as a commodity, with little emphasis on brand differentiation. However, as the market...
Eyes on Thailand in the Global Medical Cannabis Scene: SOMAÍ and Cali Dior Lead the Revolution
Global medical cannabis markets are exploding, and the patients exploring cannabis as an alternative therapy are more diverse than ever....
Q4 2024: Global Medical Cannabis Continues To Soar
The global cannabis industry saw an incredible end to 2024. Q4 2024 showed that the international medical cannabis explosion is...
SOMAÍ Joins Forces with Dascoli to Advance Swiss Medical Cannabis Market
Expanding its global footprint, SOMAÍ continues its European growth with a Swiss market entry through a strategic partnership with Dascoli...
The lobsterpot podcast S.4 EP. 1 wih Michael Sassano
SOMAÍ’s CEO, Michael Sassan, joins The Lobsterpot Podcast for an in-depth conversation on the future of Europe’s cannabis markets as...
U.S.-style cannabis dispensaries are sweeping global medical markets
Medical cannabis markets around the world are starting to show signs of early United States and Canadian-style progressions. Consumer flower...
2025 Cannabis Predictions: The Global Medical Cannabis Explosion Continues
2025 is poised for a massive explosion in the global medical cannabis market. Many politicians and regulators have been grappling...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals and PACCAN Join Forces to Transform Medicinal Cannabis in Asia and Beyond
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals partnered with Pacific Cannovation Company Limited (PACCAN) to transform Thailand into a global hub for high-quality medicinal cannabis...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Redefines Patients Experience with the Launch of Origins and Senses Lines
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, a leading EU-GMP vertically integrated Multi-Country Operator (MCO) company, proudly announces the global launch of its Origins and...
Portugal em Direto – Maior Empresa Da Europa Está Em Portugal
RTP1 – Portugal em Direto about SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
Portugal é o “epicentro do cultivo e produção de canábis”, revela CEO da SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
Com uma das maiores infraestruturas para cultivo e produção de canábis, Portugal é o maior exportador europeu desta planta para...
Cannabis industry predictions 2025: Market trends
Although new states continue to implement medical and adult-use cannabis programs, sales have been declining in the early adopters of...
The Grünhorn and Canymed Edge: Introducing Germany to SOMAÍ Extracts
Germany is one of the fastest-growing global medical cannabis markets. Recent changes in cannabis legislation have allowed doctors to more...
Business of Cannabis: Podcast | Releaf x SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
Releaf Clinic and SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals have joined forces to provide UK patients with the largest portfolio of cannabis-based medicinal products...
2025 Czechia Cannabis Predictions from Cannafest
Czechia has a population of roughly 11 million people, and cannabis has been decriminalized since 2010. As one of the earliest...
Público: Michael trouxe a experiência da cannabis medicinal do Nevada para o Carregado
Portugal já exportou este ano quase 19 toneladas de cannabis, sobretudo para a Alemanha. Em Outubro, existiam 37 entidades licenciadas...
Compounding the Issue: Germany’s Medical Cannabis Market Needs a New Approach
Germany has some of the most progressive cannabis rules in the global markets. The cannabis industry is celebrating decriminalization, which provides...
Michael Sassano: Spain finally opens access to medical cannabis
After three years of political delays, Spain has taken a big step toward starting what it promised in terms of...
The Good, the Bad, and the Profitable: Inside Germany’s EU-Leading Medical Cannabis Industry
The growth of the German medical cannabis market is poised to be highly profitable for the country. One billion euros...
The AusCannaPodcast S2 | E8 with Michael Sassano
In this episode of the AusCannaPodcast, Christina Mc Mullan sits down with Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman of SOMAI Pharmaceuticals,...
Poland’s Path to Cannabis: Two Companies Meeting Market Demands
Poland is the fastest-growing new cannabis market in the entire global medical space. Not only is the extracts market growing...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals e Universidade Lusófona colaboram em publicação científica sobre o efeito ‘entourage’
A indústria da canábis medicinal continua a evoluir, com a investigação a abrir caminho para aplicações terapêuticas inovadoras. A SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals,...
Two Cannabis Vertical Powerhouses Partner to Optimize Patient Experience
When two great companies pair to create the best patient experience possible, the global CBPM industry must take notes. Ultimately,...
Michael Sassano: “Portugal is the epicentre of cannabis cultivation and production. This is a place that will thrive”
Michael Sassano’s main goal at SOMAÍ is to produce the most advanced products with the most innovative administration routes, to...
European Cannabis Q3 2024 Quarterly Update
“WOW” is the only word to describe the excitement buzzing around the European cannabis community. The cannabis markets in Europe...
Impairment Vs Presence Of Cannabis: The International Cannabis Driving Debate Continues
Around the world, the debate continues about how to quantify the presence of cannabis in an individual’s system and how...
Give and Toke: Excitement in Global Markets w/ Michael Sassano (SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals)
Listen to the latest episode of the Give and Toke podcast, which elevates the conversation about cannabis to a higher...
Drug Science: What is the UK medical cannabis industry looking like in 2024?
We are 6 years on from legalisation of cannabis-based medical products in the UK and although many patients have now...
EU Medical Cannabis Meets Recreational Choice: A New Era in European Preference
Europe has been one of the most interesting cannabis markets to watch develop: What was a pure medical cannabis market has...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Announces Partnership with Releaf Clinic to Bring Innovative Cannabis Solutions to UK Patients
This collaboration marks the synergy of two vertically integrated fast-growing companies. SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is proud to announce a strategic partnership...
Innovations in Cannabis Extracts Entice New Demographics
Interesting trends emerge when we examine the largest extract markets in the global cannabis industry. These trends suggest that innovations...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Launches in Ireland, Offering the Broadest Range of Cannabis-Based Medicines to Patients
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals (“SOMAÍ”), a leading EU-GMP vertically integrated Multi-Country Operator (MCO) company with a global footprint of distribution for the...
What Does the Future Hold for UK Cannabis?
After a recent conversation with Pierre van Weperen of Grow Group PLC and Grow Pharma, his vision of the United Kingdom’s...
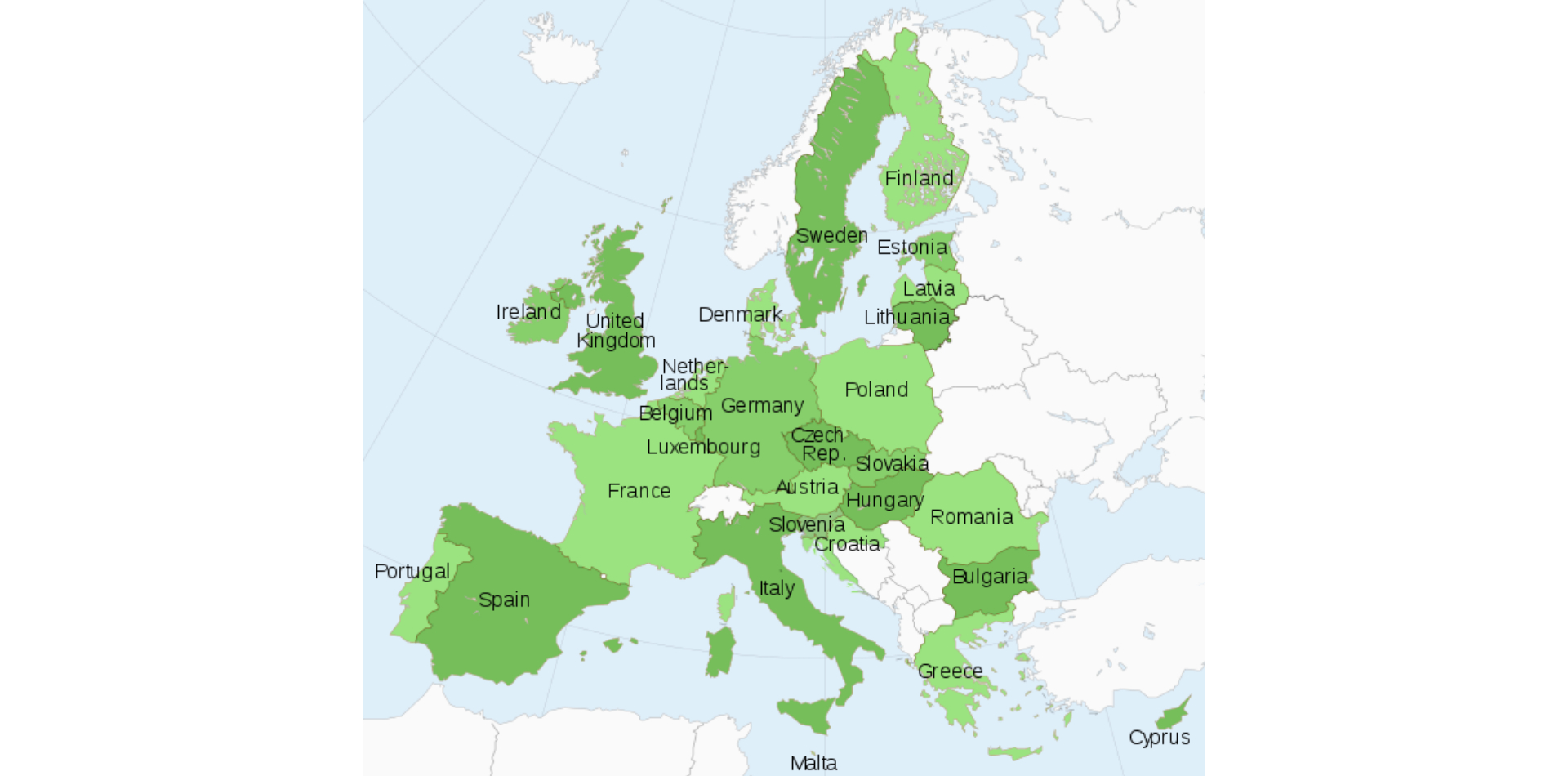
EU verticals create new European MCOs: Multi-Country Operators
New European MCOs: Multi-Country Operators European cannabis markets are heating up, and virtually every country is buzzing about regulatory change...
The Best Global Cannabis Markets By Country 2023-2024
The global cannabis universe continues to expand rapidly after the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) report, Germany’s removal...
Global Cannabis: Michael Sassano, CEO and Founder at Somai Pharmaceuticals (AltMed Ep.117)
Watch the latest AltMed podcast, in which Michael Sassano and Andrew Dowling, AltMed’s co-founder, discuss different aspects of the global...
The battle for Australian-grown cannabis: quality vs global price wars
There is a buzz around Australia about “Made in Australia” products, including cannabis. Every country should be proud of its...
Cosma S.A. and SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals partner to Revolutionize Poland with the most Innovative Cannabis-Based Solutions
LISBON, PORTUGAL, August 29, 2024 – Cosma S.A., a leader in cannabis-based pharmaceutical advancements, and SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, a fully vertically...
Hanf Journal: Interview mit Michael Sassano, CEO von SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
Cannabis-Extrakte haben sich als vielversprechendes Therapeutikum in der modernen Medizin etabliert. Allerdings werden viele Anwenderinnen und Anwender vom Geschmack abgeschreckt,...
ICBC News: Legal Global Cannabis Products Are Becoming More Diverse
As the legal cannabis industry continues to expand to nearly every corner of the planet, the variety of products available...
What is Spain’s New Medical Cannabis Regulatory Framework?
Ultimately, patients deserve access to safer alternatives to current over-prescribed pharmaceutical medicines. Spain has become the latest large European country...
2024’s Hottest Global Medical Cannabis Market Trends
A massive dose of energy has jolted the global cannabis markets. The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)...
European Cannabis Q2 2024 Quarterly Update
2024’s second quarter transpired strongly and predictably after the positive news of the 252-page United States Department of Health and Human...
CannaReporter: SOMAÍ’s Journey to Global Leadership in Cannabinoid Extracts
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is a leading EU-GMP European vertically integrated Multi-Country Operator (MCO) company with a global footprint of distribution for...
Sassano: Why future EU medical cannabis branding is essential
Michael Sassano is a CEO and Chairman of the Board for SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, a leading EU-GMP European pharmaceutical and biotech...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Expands Its Most Comprehensive Medicinal Cannabis Portfolio With Launch of New Mint Oral Solutions Line
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals (“SOMAÍ”), a fully vertically integrated Multi-Country Operator (MCO) in the global medical cannabis markets, is proud to announce...
Financial Times: European cannabis companies start IPO planning as US considers looser rules
A number of European cannabis start-ups are planning to go public in New York to take advantage of a US...
Put Some Mint Terpenes In It
What is the first thing you do when you open a new bag of cannabis flower? You smell it! Cannabis...
Cannabiz: SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals ‘keeps promise’ to deliver expanded product range
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is rolling out a suite of new products in Australia as it aims to back up its pledge...
Germany Leads The Global Medical Cannabis Explosion
The entire cannabis community is abuzz with German legalization. Not only is this a massive windfall for cannabis producers around the...
A Comparison Of Legal And Illicit EU Cannabis Markets
Co-Authored by Michael Sassano and Callum Kellas The cannabis illicit market existed in all countries long before the legal markets...
Pillar 2: German Cannabis Legalization is Moving Forward Fast
As if 2024 didn’t give the global medical cannabis enough with a 252-page report from the United States Department of Health and...
European Cannabis Q1 2024 Quarterly Update
2024 ushered in one of the most reformatory changes that the global medical cannabis community has ever witnessed. The EU...
Business of Cannabis: Breaking Down Barriers to Medical Cannabis in the UK
UK medical cannabis patients are facing multiple challenges that are preventing the adoption of the legal market. From stigmatisation and...
Medical Cannabis Goes Global: Michael Sassano of SOMAÍ reflects on UK launch (GC S2E7)
Discussing a range of topics, including Michaels’s background in setting up medical cannabis cultivation facilities in the US, The SOMAÍ...
Leading Canadian Cannabis Brand Ghost Drops Enters into an Agreement with SOMAÍ Group for Global Distribution
The partnership opportunely positions Ghost Drops and SOMAÍ Group to succeed in the EU, UK, and Australian Cannabis Markets LISBON,...
SOMAÍ Group, and its subsidiary, RPK Biopharma expand Cookies partnership to include Europe and the UK
SOMAÍ Group (“SOMAÍ”) and its subsidiary, RPK Biopharma expanded their existing partnership with Cookies Creative Consulting & Promotions, Inc., a...
Cannabis Rescheduling: DEA’s Decision Marks a New Era for the Industry
The US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is set to approve the rescheduling of cannabis in a move set to have...
The Medical Cannabis Explosion Just Got Real
The global cannabis trifecta has hit! The United States has finally rescheduled cannabis, moving it to Schedule III; the Department...
EU STARTUP NEWS: Reshaping EU’s Biopharma Industry: Is Cannabis the Future of Pharmaceutical Treatments?
While the boundaries of pharmaceuticals continue to expand with cutting-edge innovations, Lisbon-based company SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is trailblazing in the field...
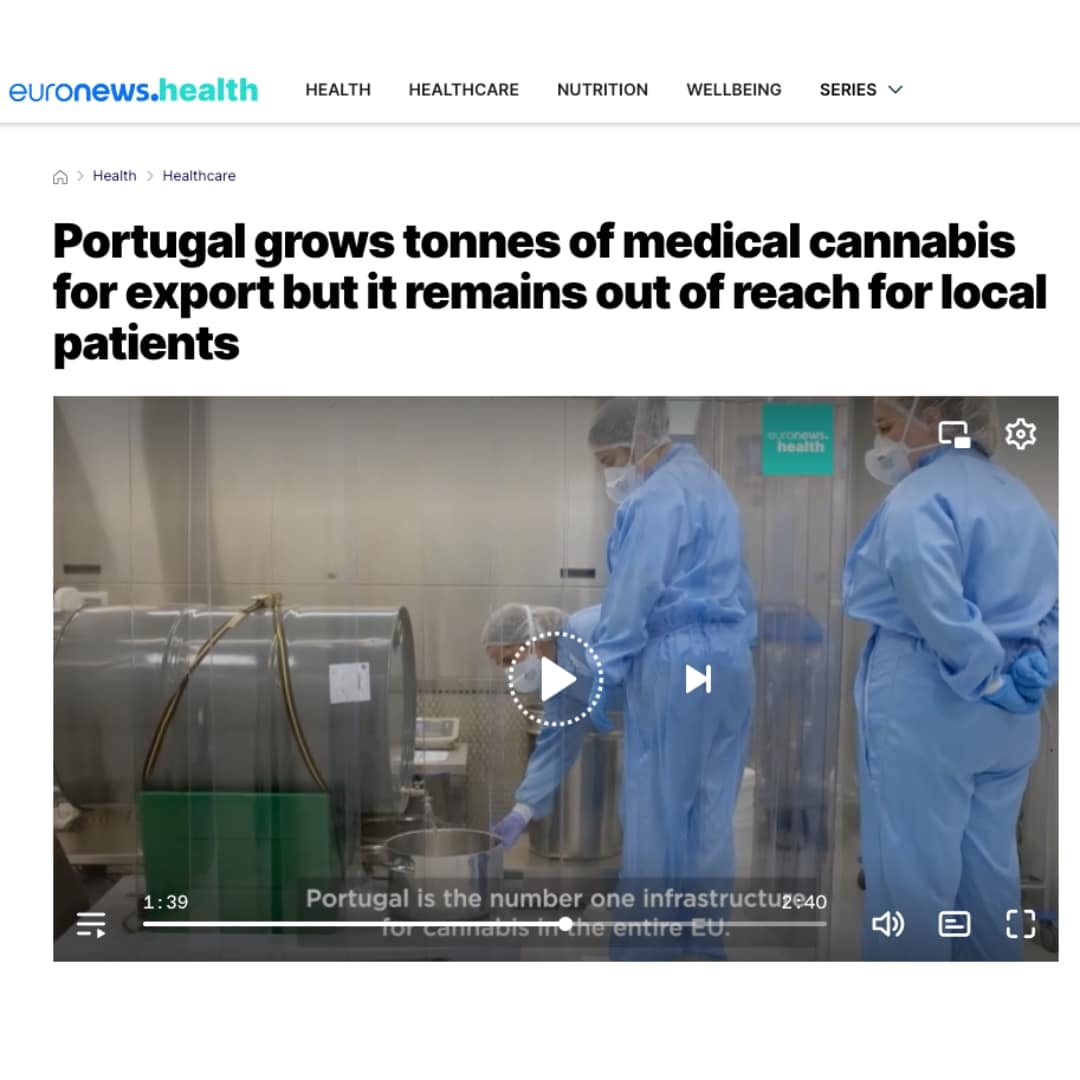
Euronews: Portugal grows tonnes of medical cannabis for export but it remains out of reach for local patients
“We’re a global company and as countries develop, we plug into that. We are still waiting for Portugal but it’s...
Japanese Cannabis Reform Is Almost Here
In November 2023, the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) was tasked with developing rules and standards for THC levels...
Assessing Thailand’s Massive Cannabis Market Reality
The Thai cannabis market is currently a full-blown recreational model, and it has exploded quicker than any market in legal...
The Global Medical Cannabis Explosion Is Coming
Based in Lisbon, Portugal, Somai Pharmaceuticals is a large-scale, GMP-certified manufacturer and global supplier of cannabis products used in pharmacological...
When it comes to access, the rest of the world should follow Australia’s example
The Australian medical cannabis industry may have its challenges, but its focus on affordable access and patient care make it...
The Surging Tides Of Global Medical Cannabis Markets
You may not see it or even hear about it but have no doubts: an enormous regulatory framework tsunami pushing...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Introduces UK to The Most Complete Cannabis-Based Product Portfolio Following a Distribution Deal
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Signs Distribution Deal with Grow Pharma for UK’s Most Comprehensive Range of Cannabis-Based Medicines LISBON, PORTUGAL, March 12,...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals brings innovative product portfolio to Australia
European medicinal cannabis manufacturing powerhouse SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is set to shake up the Australian market with a range of products...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals brings innovative product portfolio to Australia
European medicinal cannabis manufacturing powerhouse SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is set to shake up the Australian market with a range of products...
Ukraine joins global cannabis community
Now that Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy has signed a law opening access to medical cannabis, Ukraine has joined a list of...
European Cannabis Q4 2023 Quarterly Update
U.S. and German Events Steer International Cannabis in 2024 As 2023 ended, all eyes remained glued on the United States Schedule...
Don’t get caught on the hop by HLVd
As Hop Latent Viroid is discovered in Australian cannabis crops for the first time, SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals founder, chairman, and CEO Michael Sassano shares advice...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Acquires RPK Biopharma (Holigen), Reinforcing Global Leading Position in Medicinal Cannabis Sector
This strategic acquisition enhances SOMAÍ’s capacity with best-in-class cultivation, manufacturing, and distribution assets, making it one of the few verticals...
The Global Medical Cannabis Explosion is Imminent
Recently, I have become more optimistic about the global landscape of medical cannabis and the direction in which major regulatory...
2024 New Global Emerging Cannabis Markets Predictions
“As the entire cannabis world is abuzz and cannabis stocks are shooting through the roof with the potential United States...
Good or bad taste will make or break your cannabis product
When it comes to creating the ultimate cannabis brand, it’s all a matter of taste, says SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals founder, chairman,...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Introducing the U.S. Award-Winning Airo Brand to European and Australian Markets
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals announces its partnership with AIRO BRANDS, a U.S. multi-state CPG company focused on proprietary cannabis products. LISBON, PORTUGAL,...
The Mary Jane Society Podcast: Michael Sassano On Europe’s Cannabis Market
SOMAÍ Pharmaceutical‘s CEO Michael Sassano explores why the bill is a double edged sword, marking positive progress on one hand, but...
US Cannabis Rescheduling Primed to Set Off a Global Cannabis Explosion
Written by Michael Sassano, CEO, Somai Pharmaceuticals. Published in Business of Cannabis. On January 12, the United States Department of Health and...
Looking to expand overseas? Here’s what you need to know
Cannabis has long been trending as a global product, providing regional players with the chance to expand into international markets. Somai...
Why 2024 Will Be the Best Year Yet for Cannabis Investment
Year over year, global cannabis revenues exceed expectations and now stand at an estimated $50 billion in global sales in...
How Australian Cannabis Brands Can Enter Europe
Cannabis has long been trending as a global product, providing regional players opportunities to reach outside their home countries and...
Ukraine Makes ‘Historic Decision’ to Legalise Medical Cannabis
“Ukraine is headed towards cannabis legalisation which will align themselves next to German cannabis reform. As pivotal as Ukraine is...
Ukraine Lawmakers Vote to Legalize Medical Marijuana
Ukraine’s parliament voted today to legalize medical marijuana. This vote comes after the war with Russia left thousands of people...
Ukraine Lawmakers Vote To Legalize Medical Cannabis
“Ukraine legalizing cannabis should be a signal to all countries that prohibit medicinal cannabis, that there are much worst things...
The Future of European Medical Cannabis Dispensaries
As Switzerland opens up its first cannabis dispensary, cannabis pharmacies in the European Union need to pay attention and look...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals and Canify Announce Their Partnership to Introduce a Cannabinoid-Based Product Line in Germany
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals and Canify AG announce their strategic partnership to introduce a differentiated cannabinoid-based product line in Germany LISBON, PORTUGAL,...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Enters German Market with Strategic Partnerships Securing €10 Million 2-year Distribution Deal
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals announces two significant partnerships with Canymed GmbH and Grünhorn, as part of its entry into the German market....
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is thrilled to partner with the groundbreaking medical cannabis study, T21
Launched in 2019 by Drug Science, and now over 4000 patients in, T21 is building the scientific evidence base for...
3 main contributors to the entourage effect for cannabis consumers to consider
There is much talk surrounding the “entourage effect” in the cannabis world. The entourage effect is the proposed idea that...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Signs Manufacturing Contract with Canna Forest
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals has signed a manufacturing agreement with Canna Forest to produce EU-GMP-certified extracted cannabis APIs and products at its...
Q3 2023 European And US Cannabis Update
In the new edition of the “Q3 2023 European And US Cannabis Update,” SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Founder and CEO Michael Sassano...
Four things to know for properly dosing oral cannabis formulations
As oral cannabis solutions become more popular, Michael Sassano CEO and founder of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, explains how to get the...
Why white-labelled EU cannabis brands will fail
The European Union and global markets have invited the next cannabis disaster by disguising asset-poor brands as distributors and clinics....
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Makes ‘Significant Step Towards Revenue Generation’ As Portuguese Market Heats Up
Last month, Portugal’s government announced plans to establish a working group to explore the regulation of adult-use cannabis, with a...
What is Medicinal cannabis
What are the key components of medicinal cannabis?
What is the story behind Medicinal cannabis?
The endocannabinoid system
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals: recent developments in the eyes of Michael Sassano
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is a large-scale manufacturer of cannabis products, focusing on the highest quality medical-grade uses. They separate and purify...
Cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system
What does the medicinal cannabis landscape look like today?
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Receives EU-GMP Certification and Raises €5 million
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA, the largest European pharmaceutical cannabis product manufacturer, is pleased to announce that it has received authorisation...
Crude FECO Vs Distillate Extracts: What Do Consumers Really Prefer?
Last week, Germany took the first step towards wholesale cannabis legalisation after the federal cabinet waved through the long-awaited draft...
Australian medical cannabis prioritises growing patient access
The Australian cannabis market is one of the largest, fastest-growing and most robust medical industries outside North America. Australia’s market...
How cannabis could help manage the unmet need in endometriosis
Endometriosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects 10% of all women between the ages of 12 and 80 years...
Evolving legislature
Safety of medicinal cannabis and its side effects
What is Next After the German House Passes Cannabis Reform?
Last week, Germany took the first step towards wholesale cannabis legalisation after the federal cabinet waved through the long-awaited draft...
Europe’s current and future cannabis distribution models
Cannabis distribution companies in Germany and England received much attention and funding in early 2022. The growing revenue led investors to...
What are the barriers facing Spanish medical cannabis access?
Following another recent disappointment for Spanish patients, Michael Sassano, CEO and founder of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals explores the barriers preventing the...
From investor to innovator: Michael Sassano’s journey with SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
In a recent chat with Michael Sassano, the CEO of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, we delved into the intricacies of the cannabis...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals has renewed the partnership with Lusófona University/CBIOS for formulation development
According to this partnership, Lusófona will develop lab-scale formulations and perform corresponding stability testing. The collaboration will also encompass “In...
Albania Officially Green Lights Medical and Industrial Cannabis Cultivation
Albania has become the latest European country to officially legalise the ‘cultivation and processing of the cannabis plant and the...
European Cannabis Q2 2023 Quarterly Update
Country access schemes were simmering in the EU. Pressure continues to build from patients and advocates to increase access to...
WHAT IS THE CANNABIS EDGE IN GERMANY, AUSTRALIA, AND THE UK
Increasingly, global cannabis markets are moving toward regulated operations and have much to teach each other. Regulators around the world...
Cannabis Biotech: Charting the Future of Scientific Discovery
Michael Sassano, the Founder of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, discusses the latest advancements in cannabis biotechnology and explores the opportunities and challenges...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Signs Supply Contract with Cosma Cannabis
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals has entered into a two-year supply agreement with a well-respected Polish distributor Cosma Cannabis. Cosma produces medical-grade cannabis...
May 2023
SOMAÍ has been highly active as we continue to make significant strides toward our highly anticipated product launch scheduled for...
Global Whispers: A global market access journey in cannabinoid pharmaceuticals
Michael shares his company’s experiences bringing new products to market, the challenges SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals have faced and the lessons the...
April 2023
SOMAÍ has had another thrilling and eventful month as we approach our product launch in the second half of 2023....
Who Was The Winner With German Recreational Light? Pharmaceutical Cannabis
Germany has finally come out with their proposed regulation, and the clear winner is pharmaceutical EU-GMP cultivators and manufacturers. April...
GMP# 18: Sales Planning for Pharmaceutical GMP Facilities
All startups, including new pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, need to grapple with the complexities of launching. Pharmaceutical products are a considerable...
March 2023
SOMAÍ has had another thrilling and eventful month as we approach the launch of our first products in just a...
Listen Up, Startups Episode 11: Next Generation Biotech with Michael Sassano
Humanity’s healthcare needs are evolving faster than most of us can keep up with. And while many seem to be...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP# 17: GMP Market Forecasting and Budget Management
Cannabis Law Journal The process of forecasting is complex when you want to bring a new medicine to market. GMP...
Why North American medical cannabis can’t compete globally
KevinMD The United States and Canada started a movement that began as medical cannabis and quickly exploded into adult-use cannabis...
European Cannabis Q4 2022 Quarterly Update
TalkMarkets If the third quarter was painfully slow, the fourth quarter of 2022 was absolute torture for cannabis markets in...
Medicinal cannabis: Why more clinical trials and better access is needed
Drug Discovery World Michael Sassano, CEO at SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals looks at what’s needed throughout Europe to help increase access to...
Interview with Michael Sassano
Idea Wins Michael Sassano is one of the most respected executives in the pharmaceutical cannabis space today. He was an...
What start-ups can learn from highly regulated industries
Startup Observer Start-ups operating in highly-regulated sectors, like the world of pharmaceuticals, have to navigate many more obstacles compared to...
Europe’s booming cannabis industry
European Pharmaceutical Manufacturer Michael Sassano, founder, CEO and chairman of the board, Somai Pharmaceuticals, discusses the European medical cannabis sector,...
A Very Unhappy Christmas
Technical420 All through the house, not a creature was stirring—not even a Congressperson as time ran out to advance cannabis...
High prices, beating the black market, lack of education: “The European cannabis market has a long way to go”
MMJ Daily “A major benefit is that the European industry can learn from the work that has already been done...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP # 16 – Waste Reduction Management in Good Manufacturing Practice
Cannabis Law Report The pharmaceutical manufacturing industry is one of the largest waste producers in the world. In the past,...
Pharmaceutical Cannabis and The Influence From Big Pharma – Grassroots Marketing
Cannabis Radio Grassroots Marketing discusses Pharmaceutical Cannabis and The Influence From Big Pharma with Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals.
International Cannabis Reform Ramps Up in Europe, South America
The Fresh Toast The majority of the world appears to be moving towards some form of cannabis regulation, with an...
An entrepreneur’s guide to the recreational cannabis market in Europe
Cannabis Wealth Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals reflects on Q3 2022.
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP #15 – Quality Control Laboratory Optimization in GMP
Cannabis Law Report The management of a Pharmaceutical Quality Control Laboratory is a complex task that contributes to monitoring and...
Glassroots Marketing Podcast: Pharmaceutical Cannabis and The Influence From Big Pharma
Grassroots Marketing discusses Pharmaceutical Cannabis and The Influence From Big Pharma with Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals. Michael is the CEO...
The Right Way to Start A European Cannabis Business
Benzinga As the cannabis wave envelopes Europe, so too are entrepreneurs rushing to capitalize on the next biggest market in...
International Cannabis Reform Ramps Up in Europe, South America
Green Market Report Many countries waiting to see how efforts unfold elsewhere. Global cannabis reform is gaining momentum. What started...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP #14 Client Management in GMP
Cannabis Law Report Pharmaceutical cannabis companies with industrial manufacturing facilities operate in a global market and can cater to a...
Green Peak Podcast: Somai Pharmaceuticals LTD With Michael Sassano
Michael Sassano is one of the original movers and shakers in the cannabis industry. He was an early investor in...
Somai Pharmaceuticals LTD With Michael Sassano – The Green Peak Podcast hosted by Richard Zwicky
Apple Podcasts Michael Sassano is one of the original movers and shakers in the cannabis industry. He was an early...
7 Ways to Increase Terpene Levels in Cannabis
Leaf Retailer Terpenes are yet another compound found in the cannabis plant that greatly impact how certain strains taste and...
Germany’s Move To Legalize Marijuana Will Spark A Wildfire In Europe, Says This Cannabis CEO
The Fresh Toast “Germany has long been the leader in medical cannabis reform and all the other countries in EU...
Germany’s Move to Legalize Marijuana Will Spark a Wildfire In Europe: Mike Sassano
My Cannabis According to Mike Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceutical, this move is likely to spark a wildfire across Europe....
Germany recreational cannabis winners and losers
Cannabis Wealth Michael Sassano, CEO of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA, shares his thoughts on recreational cannabis reform in Germany. Leaks...
42_Watch Out. Europe Is Gaining Ground Over The U.S. In Cannabis Medicine
Listen to Michael Sassano who is one of the most respected executives in the pharmaceutical cannabis space today. He was...
European Cannabis Q3 2022 Quarterly Update
Talk Markets The third quarter for European cannabis was painfully slow and uneventful. What started as an exciting, promising year...
Is It Really Hard To Start A Business When You’re Over 50?
Forbes You’d be amazed how many people want to be entrepreneurs. You’d be even more amazed to learn this enthusiasm...
Do Any States Face The Risk Of A Dominant Cannabis Market Operator?
Benzinga Is the American cannabis sector facing the prospect of just a few players dominating the market? While worries abound...
CBD Health Podcast Episode #47- Listen to Michael Sassano who’s the international cannabis industry leader
CBD Health Podcast with Dr. Thomas Rocco Listen to Michael Sassano who is one of the most respected executives in...
Let’s be Blunt with Montel – INTERNATIONAL CANNA | MICHAEL SASSANO
Let's be Blunt On this episode of Let’s be Blunt, Montel talks with Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals, a...
Michael Sassano Exclusive Interview With TheCelebrity.Online
TheCelebrity.Online Michael Sassano is the founder, chairman and CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals. Michael Sassano is also an invester and expert...
Cannabis Crossing Borders: Global Flower Trade in 2022
Ganjapreneur In less than a decade, the cannabis industry has gone from seeing a worldwide blanket prohibition of the plant...
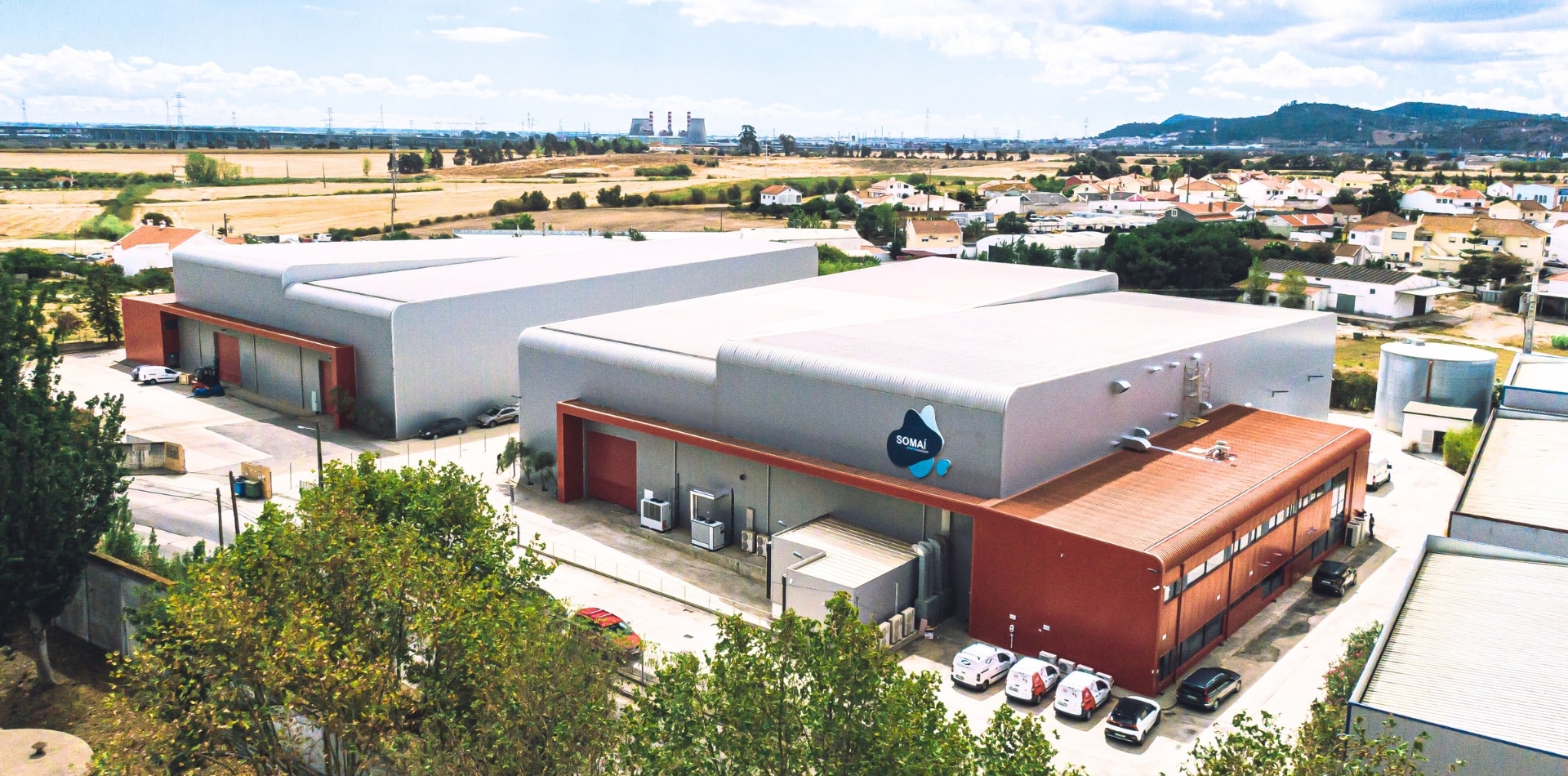
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Opens Portugal Manufacturing Facility
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has officially opened its new state-of-the-art pharmaceutical EU-GMP facility in Portugal.
The Mary Jane Society Podcast – Watch Out. Europe Is Gaining Ground Over The U.S. In Cannabis Medicine
Mary Jane Society Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals, a European pharmaceutical, and biotech company centered on manufacturing in Lisbon,...
Schumer is still committed to cannabis banking reform
Business of Cannabis The House sponsor of the Secure and Fair Enforcement (SAFE) Banking Act, Rep. Ed Perlmutter, says he...
Germany’s Adult Use Cannabis Laws Steeped In Optimism And Uncertainty At The Moment
Benzinga Impact of Possible German Cannabis Legalization If Germany legalizes adult use, a wave of benefits could come to the...
To Be Blunt: The Professional Cannabis Business Podcast – Episode 117: The Global Cannabis Market and Why Germany is Poised to Lead
To Be Blunt “If Germany goes recreational, everybody's going to follow them to some extent. If the leader says, look,...
The Investor Talk – with Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman for SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals
Equity Match Episode 29: Watch the #TheInvestorTalk episode with Michael Sassano Michael Sassano, the Founder, Chairman & CEO of Somai...
Inside Europe’s largest cannabis manufacturing facility
Sifted Walking around Europe’s largest cannabis manufacturing facility, it quickly becomes obvious that I’m in the hands of a veteran....
Making the Best Concentrates For a Global Market
Maximum Yield Article by Anthony Demeo and Michael Sassano The global market is waking up to quality concentrates and extracts,...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP #13: Preventive Maintenance in GMP
Cannabis Law Journal Consistent and reliable pharmaceutical manufacturing depends on many factors, but a critical one is the process equipment....
Michael Sassano of Somai Pharmaceuticals on To Be Blunt – Episode 117 The Global Cannabis Market and Why Germany is Poised to Lead
Shayda Torabi - YouTube Michael Sassano of Somai Pharmaceuticals on To Be Blunt
Karma Koala Podcast Episode 92: Professor June McLaughlin, Kim Stuck Allay Consulting, Michael Sassano Somai Pharmaceuticals & Amy McDougal Clearsources
Spotify Heather Allman talks with Michael Sassano of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals LTD about recent regulatory changes, the differences between Europe and...
Interview Time! Michael Sassano – CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals
YouTube - Ask GenieNansea In this episode, SOMAÍ's CEO, Michael Sassano, explains how he got involved in the industry, talks...
With Extracts Expected To Achieve A ‘50% Share Of The EU Cannabis Market’ In The Next Few Years, Who Is Currently Leading The Field?
BusinessCann Michael Sassano, CEO of international cannabis manufacturer Somai Pharmaceuticals, explores the state of cannabis extract manufacturing in Europe and...
The Case for THCA and Other Minor Cannabinoids
Cannabis Science and Technology In this article, Somai's R&D Director, Anthony DeMeo, examines why we should be studying cannabinoids beyond...
Consider Cannabis – Cannabis and International Markets
Consider Cannabis
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP #12: Optimizing Pharmaceutical Good Manufacturing Processes
Cannabis Law Report Manufacturing process optimization aims to increase productivity, decrease operational costs, and make the manufacturing process more robust...
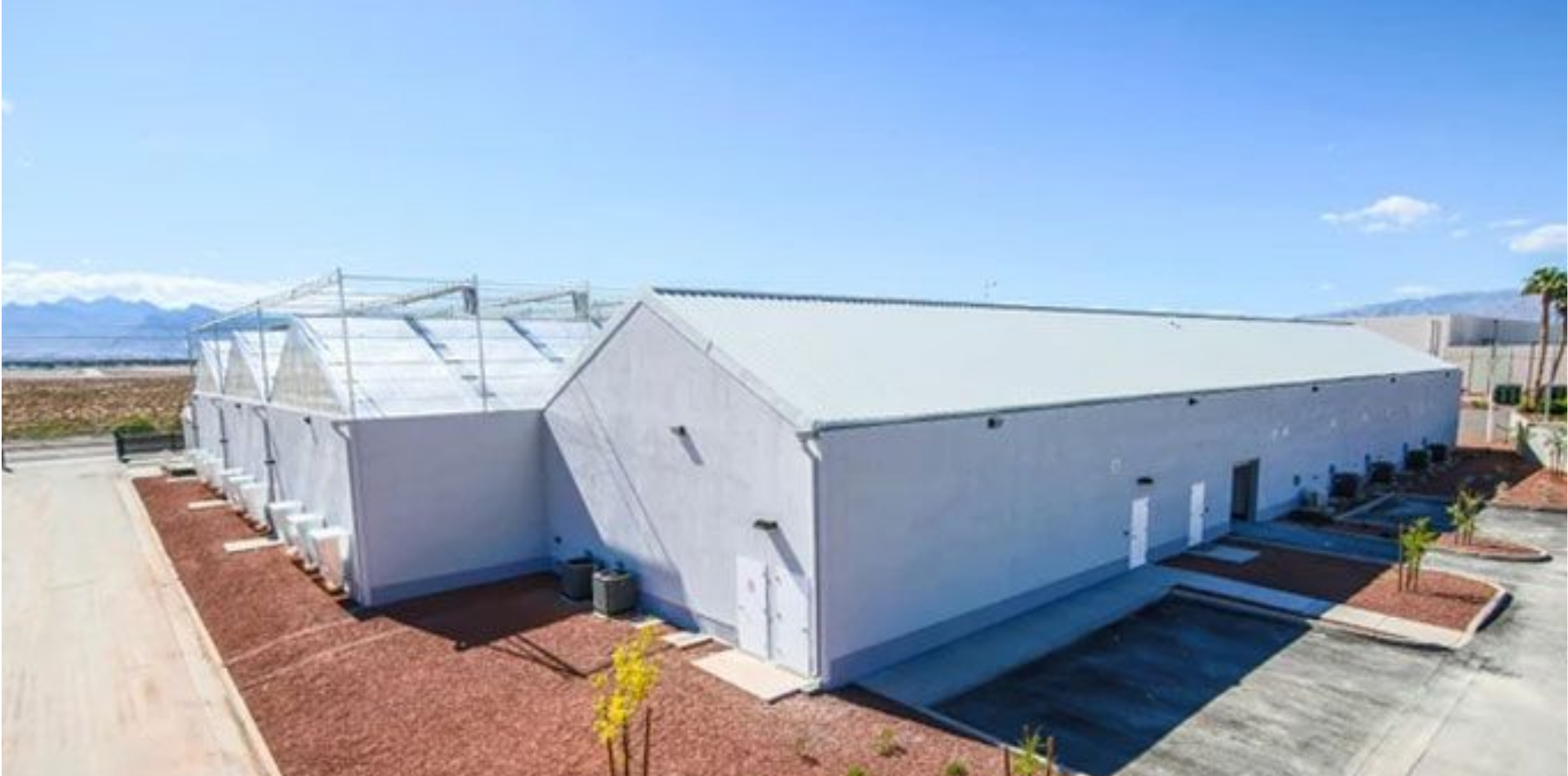
SOMAÍ PHARMACEUTICALS – MEDICAL CANNABIS PRODUCTS MANUFACTURING FACILITY
Anteprojectos Como primeiro investimento da SOMAÍ em Portugal, foi apresentado um edifício com licença de armazém, com a pretensão de...
Here Weed Go – It’s Pharmaceutical (in Europe)
Omny Studio Today’s episode has a decidedly European flavor: my guest is Michael Sassano, the Founder, Chairman and CEO of...
The Israeli Cannabis Market Is Growing Faster than People Realize
Technical420 I recently had a chance to visit Israel and learn about the Israeli cannabis market from the best growers...
European Cannabis Regulators Ease Restrictions in Preparation of EU Green Wave
Cannabis Business Times Changing laws and regulations in countries such as Germany, Switzerland and Spain indicate increased cannabis access for...
Vertical Integration: Cannabis Experts Discuss Its Various Pros And Cons
Benzinga Vertical integration in the cannabis industry is one of the most debated topics of the day across the sector....
ICBC Berlin 2022 B2B Conference Panels Day 2 | Cannabis In Biotechnology
YouTube - International Cannabis Business Conference Are cannabinoids and other cannabis active ingredients a building block for the biotechnology of...
Disposable Vapes Are An Environmental Concern But Producers Won’t Stop Making ’til You Stop Buying
Benzinga Annual cannabis vape sales continue to grow across many major markets–fueling demand and a growing eco-footprint. Rising consumer demand...
European Cannabis Q2 2022 Quarterly Update
The second quarter in Europe far outpaced the first quarter in market movements regarding legislative country news and Merger &...
SAFE Banking Act Dropped From China Competition Bill
High Times A bill to allow financial services to businesses in the legal cannabis industry was dropped from a China...
Switzerland Removes Medical Marijuana Access Limitations As Demand Rises
Benzinga The Swiss government confirmed that it will remove limitations on medical marijuana use, starting August 1st, 2022. Medical marijuana...
Switzerland set to lift medical cannabis restrictions
Leafie The Swiss government announced today that it will lift restrictions on cannabis for medical use from August 1st 2022....
Cannabis Insiders Split On Market Impact Of Inflation
Benzinga In the days leading up to the recent bear market entry, cannabis insiders provided Benzinga with varied opinions regarding...
Thailand removes cannabis from narcotics list, decriminalises growing plants at home
ABC NEWS Thailand has become the first country in Asia to take marijuana off its list of banned substances and...
Germany’s legalisation push has lit up the European cannabis market
Cannabis Wealth Mike Sassano, CEO of European cannabis manufacturer Somai Pharmaceuticals, offers his perspective on Germany’s accelerated plans for adult-use...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP #11: Stock Management in GMP Manufacturing
Cannabis Law Report In Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) facilities, managing your stock is critical for Quality Assurance (QA). Your QA...
The Cannabis Corner Episode 44 – Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman for Somai Pharmaceuticals
Cannabis Corner Podcast This week Michael Sassano of Somai Pharmaceuticals , a Lisbon, Portugal based cannabis pharmaceutical manufacturer , joins...
Sequire Cannabis & Psychedelic Conference 2022 – Somai Pharmaceuticals
YouTube - Somai Pharmaceuticals Sequire Cannabis & Psychedelic Conference went live on April 20th with industry experts and investor 1:1s....
CannaList Conversations with Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman for Somai Pharmaceuticals
CannaList Conversations We recently sat down with Michael Sassono - he is one of the most respected executives in the...
“Positive shock waves”: Germany accelerates process for cannabis legalisation
Cannabis Wealth Germany’s health minister Karl Lauterbach – who until last year was opposed to cannabis legalisation – said Germany’s...
CPhI North America 2022: Pharmaceutical Cannabis Global Marketplace
YouTube - Somai Pharmaceuticals Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman, Somai Pharmaceuticals presented on Monday the 9th of May 2022 at...
Michael Sassano & Antonio Guedelha: GMP Article 10: Production Cost Calculation Systems in GMP
Cannabis Law Journal When you look to the future of your company’s life cycle, financial health in planning your exact...
MGC Pharma, Cansativa Group & Somai Pharmaceuticals announced among Cannabis Europa sponsors
Pressat As cannabis makes its way into the mainstream across Europe, the continent's premium B2B cannabis industry conference - Cannabis...
European Cannabis Q1 2022 Quarterly Update
Talk Markets 2022 started with an incredible amount of progress and hope with European cannabis fast becoming a hot emerging...
How to Invest in Marijuana
U.S. News Both strides and setbacks have punctuated the quest for federal legalization of cannabis in the U.S. So far,...
Michael Sassano: GMP Article No 9: Bringing New Products to GMP Facility
Cannabis Law Journal Now that your GMP facility has been opened, it’s time to add some new products to your...
The European Cannabis Report: 7th Edition | Expert Opinions: Michael Sassano (page 34)
Prohibition Partners What is SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals? SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Ltd is a European pharmaceutical and biotech company with a manufacturing centre...
3 Reasons Cannabis Sin Stocks Stay Strong in Volatile Markets
Technical 420 As global stress and market uncertainties remain high during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, investors looking for stability...
Inflation: is it affecting the cannabis market?
Cannabis Wealth Inflation is at a record high, but cannabis prices are continuing to fall. Could cannabis be inflation-proof or...
The case for improving absorption for cannabinoids using ethosomes
Drug Target Review Michael Sassano and Anthony DeMeo from Somai Pharmaceuticals discuss using ethosomes as an improved method to deliver...
Opinion: 2022 could be the year for pharmaceutical marijuana
MJBizDaily Last year proved to be an interesting one for the entire cannabis industry. In particular, the emergence of large...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals + Huge Gage Cannabis News!
Benzinga Benzinga Cannabis Insider is a bi-weekly podcast focused on marijuana and all things weed, CBD, hemp, and psychedelics. Hosts...
Karma Koala Podcast Episode 67: This Week Michael Sassano, Inesa Ponomariovaite & Our Regular Segment From Dentons German Cannabis Head, Peter Homberg
Spotify INTERVIEW 2: Michael Sassano, who has been writing regular articles for cannabis law jnl on all things international compliance...
Innovations in Dosing Technologies: Getting an Accurate Hit, Every Time
Cannabis Industry Journal The cannabis industry has a wealth of creative talent. With the market beginning to tear away from...
Safety and Culture at Forefront of Cannabis Social Club vs. Dispensary Debate
Cannabis Business Times As the legalization of adult-use cannabis sweeps Europe, stakeholders and emerging investors on both sides of the...
Synthetic Cannabinoids versus Plant-Derived Products
Terpenes and Testing Magazine Crafting synthetic, semi-synthetic, and isomerization of cannabinoids is old hat for chemists. Natural cannabinoids are derived...
Spotlight Interview with Michael Sassano, CEO and Chairman of the Board for Somai Pharmaceuticals
Pharmashots On February 01, 2022, PharmaShots will present the second interview in its new interview section, “Spotlight- Company of the...
How Germany Can Enter The Adult-Use Cannabis Market Successfully
The Fresh Toast Germany Recreational Cannabis is Close. The new German coalition has indicated one of its many priorities is...
How Germany Can Enter The Adult-Use Cannabis Market Successfully
Benzinga Germany Recreational Cannabis is Close. The new German coalition has indicated one of its many priorities is the legalization...
Portugal Is Highly Likely To Legalize Recreational Cannabis
Benzinga Portugal has long been ahead of other European countries in its understanding and stance on drug reform, so it...
Michael Sassano – Somai Pharmaceuticals – Conforming to the Highest Pharmaceutical Standards
Valiant CEO Michael Sassano is well known as one of the original investors in the cannabis industry. He is celebrated...
Uber Eats to Offer “Baked Goods” with Canadian Cannabis Partnership
Marketscale “Every move that standardizes cannabis into the distribution and sales is a step to combatting the black market. Not...
Croptober – Navigating the Business of Cannabis Cultivation and Sustainability – Michael Sassano
YouTube - Somai Pharmaceuticals On Thursday, October 28 Excelsior College hosted a cannabis webinar, Croptober: Navigating the Business of Cannabis...
Cannabis Europa London 2021 – Michael Sassano
YouTube - Somai Pharmaceuticals At the Iconic Banking Hall in London, on 11 November Cannabis Europa returned - bringing together...
Which Countries Will Likely Legalize Cannabis In 2022 And Why Isn’t The US Among Them?
Benzinga Cannabis reform is heating up across the nation. With it comes a booming multinational market, including a projected $102...
Michael Sassano, Renowned Pharmaceutical Expert, and Founder and CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals LTD Zoom Interviewed
EIN Presswire Michael Sassano, Renowned Pharmaceutical Expert, Founder & CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals LTD Zoom Interviewed for The DotCom Magazine
DotCom Magazine Interview of Michael Sassano, CEO & Founder of Somai Pharmaceuticals LTD
YouTube - Somai Pharmaceuticals Michael Sassano is well known as one of the original investors in the cannabis industry. He...
How SOMAÍ is Bringing ‘Peak Efficiency’ and ‘Peak Profitability’ to the European Cannabis Market
Cannabis Europa Michael Sassano has been involved in everything from real estate to banking and cutting-edge tech investment. But he...
Cannabis Investment: 7 Best Marijuana Stocks to Buy for 2022
WTOP (Washington DC News) These seven marijuana stocks are on sale. Investors had high hopes for the legal marijuana industry...
Michael Sassano: GMP Series #8: Manufacturing Startup
Cannabis Law Journal Your journey maneuvering through the start-up phase of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) will finish with certification of...
Few Medical Cannabis Licenses in Portugal Have Been Awarded
High times Infarmed approves only 19 of the 114 applications for medical cannabis cultivation in Portugal. Ever since Tilray decamped...
Cannabis Co. Receives $3M ‘Innovative Products’ Grant From Government, EU In Portugal
Benzinga SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA, or SOMAÍ, recently received an “innovative products” grant of 2.7 million euros ($3.07 million). Provided...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals awarded €2.7M in funding from Portugal 2020 Grant
BusinessCann SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has received an innovative products grant of 2.7 million euros by the Portugal 2020 committee....
Projeto Nº POCI-02-0853-FEDER-179647
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has officially opened its new state-of-the-art pharmaceutical EU-GMP facility in Portugal.
EU: Cannabis company receives €2.7 million grant
MMJ Daily Somaí Pharmaceuticals has received a €2.7 million grant from the Portugal 2020 committee.
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Erhält Im Rahmen Von Portugal 2020 Fördermittel In Höhe Von 2,7 Mio. Euro
TechiLive LISSABON, Portugal, Nov. 10, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA hat vom Portugal 2020-Komitee Fördermittel für innovative...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals bénéficie d’un financement de 2,7 millions d’euros de Portugal 2020
News Bit LISBONNE, Portugal, 10 nov. 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA a reçu une subvention pour produits...
Somai Pharmaceuticals: SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals erhält im Rahmen von Portugal 2020 Fördermittel in Höhe von 2,7 Mio. Euro
Finanz Nachrichten LISSABON, Portugal, Nov. 10, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA hat vom Portugal 2020-Komitee Fördermittel für...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals awarded €2.7M in funding from Portugal 2020 Grant
Yahoo Finance LISBON, Portugal, Nov. 10, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has received an innovative products grant...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals awarded €2.7M in funding from Portugal 2020 Grant
AP News LISBON, Portugal, Nov. 10, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has received an innovative products grant...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals awarded €2.7M in funding from Portugal 2020 Grant
Opera News LISBON, Portugal, Nov. 10, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has received an innovative products grant...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals awarded €2.7M in funding from Portugal 2020 Grant
Profiles in Legalization LISBON, Portugal — SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA has received an innovative products grant of 2.7 million euros...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals bénéficie d’un financement de 2,7 millions d’euros de Portugal 2020
La Bourse Et La Vie LISBONNE, Portugal, 10 nov. 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Unipessoal LDA a reçu une...
Somai: The Global Story of Cannabis
Startup Thread I recently spoke with Michael Sassano, founder of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals, an international company focused on the extraction of...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals at MJUnpacked: What Are You Trying To Accomplish At MJ Unpacked?
CFN Media Group
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals at MJUnpacked: What Markets And Geography Does Somai Pharma Address?
CFN Media Group
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals at MJUnpacked: What Should Consumers, Other Brands And Investors Know About The Future Of Somai Pharma
CFN Media Group
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals at MJUnpacked: Tell Us About Your Company And What Makes You Different
CFN Media Group
These Are The Cannabis Industry’s Biggest Tricks and Treats So Far
Benzinga Halloween is almost here. As costumed revelers prepare for a weekend of celebrations, the cannabis industry readies for the...
Michael Sassano: GMP Series #7: Personnel Recruitment
Cannabis Law Journal No matter what you build or which equipment you purchase, your business cannot be successful without hiring...
Michael Sassano: GMP Series Part 6 – Quality Assurance Implementation
Cannabis Law Journal The difference between Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA) is not always clear. Quality Control refers...
Why Germany is Not the Future Leader of European Cannabis
Technical420 For the last several years, all I have heard about from EU cannabis producers, growers and investors is “GERMANY,...
Michael Sassano CEO and Chairman Somai Pharmaceuticals: GMP Series #5: ERP Implementations
Cannabis Law Report When tackling your computer systems, software, and quality control processes, keep in mind that there are many...
The Advantages of Ethanol Extraction
Extraction Magazine Extraction technology is constantly evolving each year, which helps drive down associated costs, increase output volumes, and improve...
Does Big Business Provide A Better Look Into Cannabis Reform Than Capitol Hill?
Business Insider Operators in various sectors of cannabis feel that the industry provides a better insight into regulatory needs and...
Does Big Business Provide A Better Look Into Cannabis Reform Than Capitol Hill?
The Fresh Toast Operators in various sectors of cannabis feel that the industry provides a better insight into regulatory needs...
Does Big Business Provide A Better Look Into Cannabis Reform Than Capitol Hill? Operators Believe So.
Benzinga Cannabis operators and executives tell Benzinga that the movement of private and public companies may serve as a better...
Cannabis Stocks Next Big Wave Is Coming Late August
Benzinga Multi-State Operators (MSOs) in the United States are primed for the next big stock amp-up, which could see at...
Michael Sassano and Antonio Guedelha: GMP Series Part 4: Laboratory Set-Up
Cannabis Law Report The laboratory is both one of the most active and one of the most critical rooms in...
GMP Series Part 3: Process Equipment Procurement
Cannabis Law Report In the next installment of the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Series, we will be exploring process equipment...
Could Drug Store Giants Eventually Sell THC? It’s Possible, But Many Hurdles Remain
Benzinga Drug store giants are already establishing themselves in the CBD market. Major players, including Walgreens Boots Alliance Inc
European Cannabis is Starting to Look Like the US Market 10 Years Ago
Cannabis Industry Journal As the cannabis industry — now estimated to be worth more than USD 200 billion — continues...
CANNA WORLD EXPO EUROPEAN UPDATE SOMAI PHARMACEUTICALS CEO MICHAEL SASSANO
Canna World Expo Empowerment 2021 CANNA WORLD EXPO is honored to have Somai Pharmaceuticals CEO, Michael Sassano, as an Empowerment...
Expert Interview: Michael Sassano, CEO Somai Pharmaceuticals
Prohibition Partners Who are SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals? SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals is an international company focused on creating unique cannabis formulations for the...
Beyond CBD, THC: ‘Minor’ Cannabinoids Flood Market — Lack of data is concerning, even for practitioners who believe in medical cannabis
MedPage Today On the heels of the cannabidiol (CBD) craze come three other cannabinoids touted as potential treatments for various...
Why GMP is the Future of Quality Control for the Global Industry
Cannabis Business Executive Good Manufacturing Practices, or GMP, are a systematic way of ensuring that products — from food to...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Bringing The Future Of European Cannabis Market
Benzinga When the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world by surprise last year, cannabis businesses around the world faced the uncertainty...
SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Bringing The Future Of European Cannabis Market
Yahoo Finance When the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world by surprise last year, cannabis businesses around the world faced the...
Morocco: Cannabis Legislation but the Devil in the Details
Fanack Morocco approved in March 2021 a law that will see a legal cannabis industry emerge in one of the...
Low-Cost Pot Stocks To Consider, According To SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals CEO Mike Sassano
Benzinga SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Ltd. co-founder and CEO Michael Sassano recently spoke to Benzinga about a particular value buy that's piqued...
Cannabis Revival and Year of the SPAC’s: What’s To Be Expected the Rest of 2021?
Cannabis Industry Journal The unusual nature of 2020 gave rise to a reciprocally roller-coaster-like cannabis market. Cannabis was cemented officially...
SPAC Mania: The Biggest Cannabis Boom Is Yet To Come
Cannabis Business Executive If you’re reading this you undoubtedly know that special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) are all the rage....
GMP Series Part 2: Building and Design – Authored By: Michael Sassano and Antonio Guedelha
Cannabis Law Report In the quest to become GMP compliant, design and flow of your manufacturing facility are critical. Mistakes...
Benzinga Cannabis Capital Conference | February 25-26, 2021 | Michael Sassano
Benzinga Capital Conference Michael Sassano, CEO of Somai Pharmaceuticals talk about the European Cannabis Market and how it is starting...
Navigating Regulatory Hurdles in Specific Countries
Cannabis Business Executive Despite Europe’s unification, each country is still making their own rules on providing access to medical cannabis...
Cannabiz: How to Invest in This Growing Industry
Ticker Tape Early February marked a big step for the cannabis industry with the announcement that Jazz Pharmaceuticals (JAZZ) will...
GMP & Compliance: GMP SERIES #1: “Starting Your GMP Approval Process for Cannabis Correctly”
Cannabis Law Report The path to facility and product approval in cannabis is a long road that requires attention to...
PREDICTIONS | Want to know the future? There are two ways: a crystal ball or really smart people (pages 74-75)
B2B Wholesaler Magazine Mike Sassano, CEO and Chairman of Somai Pharmaceutical: “2021 is shaping up to be the most explosive...
Ingenious Cannabis Entrepreneurs to watch in 2021
IdeaMensch There is way more to cannabis than getting “high.” The United States alone has grossed a total between $71.4B-$87.5B...
These Are The Top European Cannabis Companies
CBDevious The legality of cannabis for medical and recreational use varies by country, in terms of its possession, distribution, and...
9 Things to Consider When Raising Capital for Startups in Europe
Cannabis Business Executive Since my first job on Wall Street at Lehman Brothers, I was taught to raise money. And...
Tantalizing Terpenes Boost Cannabinoid Blends For The European Market (pages 20-21)
CBD Health & Wellness Magazine The recent election in the US brought sweeping changes to the cannabis industry in just...
UK to see largest medical cannabis market growth in Europe 2020 to 2025
Yahoo Finance UK Britain is set to see the greatest cannabis medical market growth rate in Europe between 2020-2025. According...
Desert Oasis | Solaris Farms is capitalizing on a prime location and plenty of Nevada sunshine (page 58-61 November issue)
MARIJUANA VENTURE MAGAZINE: Michael Sassano took everything he learned from developing real estate and put it into growing plants in...
‘The sweet spot for cannabis business opportunities is somewhere between medical and recreational’ – experts explain how to find it
Business Insider Mike Sassano, the founder of Nevada cultivation brand Solaris Farms, explained that many customers consume marijuana for medical...
Cannabis Top 20: North America’s Largest Commercial Grows
Greenhouse grower As the cannabis industry continues its evolution, North America-based growing operations are scaling up across multiple states, and...
Real Deals – Michael Sassano
Marijuana Business Magazine Now that the economic situation doesn't support unbridled growth in the industry, more cannabis companies might consider...
Best practices for securing your cannabis grow operations and supply chains
Security Infowatch The cannabis industry comes with its own set of inherent security risks, especially in vertically integrated grow operations....
Cannabis Terpenes: What Growers Need to Know
Greenhouse grower: “There’s no witchcraft to it or anything like that. It’s just kind of the whole combination of light...
Opening the Pot: Vegas Cannabis Industry Moving Ahead Amidst COVID
Millennial Magazine Vegas relies on the more than 42 million tourists to maintain its economy, so when COVID-19 (COVID) hit...
California joins push to let cannabis businesses use banks as part of coronavirus relief
The Orange County Register: California Attorney General Xavier Becerra is joining a bipartisan group of 34 attorneys general in urging...
Cannabis company executives speak to the industry’s trying times
Real Assets Adviser "The United States and worldwide trend of legal sales will only improve, since we are far from...
Why Large-scale cannabis producers are turning to Hybrid Greenhouses
Joomag "The environment can be controlled in both indoor and hybrid greenhouses in almost the exact same way, but it...
Lawmakers Look to Include Cannabis Banking Reform in Next COVID-19 Stimulus Bill
Cannabis Business Times “There is no positive in having cash outside of the banking industry for the safety of our...
COVID-19 Is Leaving Its Mark On The Cannabis Industry, Insiders Say
Huffpost Michael Sassano of Solaris Farms, a large-scale industrial hybrid greenhouse cultivator in Las Vegas says while CBD might work...
Why Cannabis Will Boom During the “New Normal”
Nisonco "In the future, the entire cannabis industry will benefit from not only it’s essential medicine title, but also hundreds...
Cannabis Do-Gooders: These Companies Are Lending A Helping Hand Against COVID-19
Benzinga “Creating a safe environment while cannabis is deemed 'essential' added tremendous positive energy for our team, while at the...
Cannabis Do-Gooders: These Companies Are Lending A Helping Hand Against COVID-19
Yahoo finance "Recently, in-order to give back to the community and create outward good will, Solaris Farms reduced pricing to...
Hemp Companies Step Up To Help During Pandemic
Hemp Market Report “Although our first priority is to the safety of our employees and doing our part to slow...
Cannabis Pros Sound Off On How Coronavirus Pandemic Will Affect Industry
Forbes Michael Sassano, founder and CEO of Solaris Farms, a Las Vegas-based greenhouse for growing cannabis, is filtering the turmoil...
CannaBusiness Tips For Coronavirus Times
Benzinga "Don’t panic, but it’s time to look at a slow down in all businesses, including cannabis sales. Recently, I...
Cannabis Executives on Turbulent Markets: “Don’t Panic”
Equities “I’m a believer in letting the flood gates open. But I see things from a well established position. The...
Michael Sassano: the man bringing US cannabis know-how to Europe
Cleanroom Technology The focus of the marketplace is on CBD, Sassano admits, noting regulation is developing. "Places like Switzerland have...
Michael Sassano: the man bringing US cannabis know-how to Europe
NBR A US native, Sassano believes a more liberal approach to the use of cannabis will take some time for...
Michael Sassano: the man bringing US cannabis know-how to Europe
Manufacturing Chemist "This declassification is more symbolic than ground-breaking," tells me Michael Sassano, Founder and CEO of Solaris Farms, a...
New Cannabis Products: Kiva’s Camino CBN Line, Solaris x Cannabis & Culture’s Line And A Topical Cream
Yahoo finance "With over $100,000 in sales the first week of launch, it’s clear that Culture and Cannabis’s reach means...
New Cannabis Products: Kiva’s Camino CBN Line, Solaris x Cannabis & Culture’s Line And A Topical Cream
Benzinga Michael Sassano, CEO of Solaris, told Benzinga, "The merger of the Culture and Cannabis media group with Solaris Farms...
European Union Urges Member Nations to Vote for World Health Organization’s Cannabis Rescheduling Recommendations
Cannabis Business Times “The 1961 Narcotics Act of Europe is similar to [the Drug Enforcement Administration’s (DEA)] Schedule I in...
“Marijuana is a global trend that can no longer be stopped.”
Incrussia The largest marijuana market in Europe is now Germany ($100 million). The American market is estimated at about $10...
Which European Countries Cannabis Investors Should Watch in the New Decade
Equities Europe is at the crawling stage of cannabis development and starting their first awkward steps with medical acceptance. -...
Solaris Farms & Tech-Driven Growing
Culture & Cannabis The cultivation is relatively new, springing up in the summer of 2016. Despite its age, Solaris Farms...
‘Big Cannabis’ Technologically Ahead Of Its Times, But Post-Harvest Automation Remains Elusive
Forbes “The tech is getting closer but we’re not there yet,” said Michael Sassano, CEO, Solaris Farms, a cannabis cultivator...
U.S. leads in cannabis innovation, but cedes global market to Canada
The Denver Post The genetics and sophistication underlying the U.S. cannabis industry lead to better-quality and higher-potency flowers for those...
American pot is the gold standard. But Canada leads the export game — for now
Salon The genetics and sophistication underlying the U.S. cannabis industry lead to better-quality and higher-potency flowers for those who smoke...
American pot is the gold standard. But Canada leads the export game — for now
Kaiser Health “The world wants that technology,” said Michael Sassano, CEO of Solaris Farms, the largest cannabis hybrid greenhouse in...
From Seed to Sale Nevada’s Cash Crop Cannabis Industry
Nevada Business Initially, no one thought growing cannabis in the Southern Nevada desert would take. But Solaris Farms is growing...
America’s marijuana growers are the best in the world, but federal laws are keeping them out of global markets
Washington Post Federal prohibitions are getting in the way of efforts to grow the U.S. marijuana business into a global...
What Should Investors Take Away From MJBizCon 2019?
Equities Marijuana Business Daily’s annual MJBizCon is the largest conference and convention in the global legal cannabis industry. This year's...
How to Do Cannabis Cultivation Business Planning for Growth
B-Plans Developing a cannabis cultivation business requires significant planning, dedication, and focus. Initially, you’ll need to develop a solid plan...
“5 Things I Wish Someone Told Me Before I Started Leading a Cannabis Business”, with Michael Sassano and Len Giancola
Medium The cannabis business is a complete dedication and you must make large sacrifices for it. It is very fast...
Key trends when investing in the Cannabis industry in Opportunity Zones
Opportunity Zone Cannabis land development is growing and gaining traction in Opportunity Zones (OZ). Not only has a large amount...
Vegas Hybrid GreenHouse Dominance by Mike Sassano – page 20
Vegas Cannabis magazine
The Cannabis Cultivation Costs by State
MG Retail Magazine To the outside world, the legal cannabis industry appears to be one big cash machine. While it’s...
Mike Sassano: Increasing Potency with Greenhouse Technology
Ganjapreneur Michael Sassano is the CEO and founder of Solaris Farms, one of three large greenhouse cannabis cultivators in Nevada....
OZ WRITERS COUNCIL DIRECTORY
OZ WRITERS COUNCIL DIRECTORY The Council is an invitation-only group of executives and professionals with experience in the Opportunity Zone...
Are cannabis hand-trimmers an endangered species?
Leafly Many people in the cannabis industry start out as trimmers. Wearing “sticky gloves” is a way to learn the...
Automation and sensors in hybrid greenhouses
AgTechTomorrow Solaris is a high tech hybrid greenhouse designed specifically for desert environments. It was the first ground up hybrid...
Desert Greenhouse Cultivation
Blunt Business Desert greenhouse cultivation with Michael Sassano Founder and CEO of Solaris Farms. Michael says they have the largest...
Five Diverse Questions With Michael Sassano, Founder: Solaris Farms
Forbes I was born and raised in Cleveland, Ohio before attending Boston University. I graduated Cum Laude with Distinction in...
Automation is the Future of Cannabis
Equities As industries evolve, the companies within them consistently work to implement new methods that update their processes so they...
How Solaris Farms’ Michael Sassano Works: Cannabis Workspace
Cannabis Business Times In this installment, CBT presents an up-close look at the tools and habits behind the Nevada-based cultivator’s...
Federal Court Orders DEA to Explain Inaction on Cannabis Cultivation Applications
Analytical Cannabis Michael Sassano, founder and CEO of the Nevada-based cannabis cultivation operation Solaris Farms, told the Cannabis Business Times,...
Federal Court Orders DEA to Explain Why It Has Ignored Cannabis Cultivation Applications
Cannabis Business Times A federal court has ordered the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) to explain why it has not responded...
Soma Pharmaceuticals Reveals Plans for Ireland’s Medical Cannabis Market
Cannabis Business Times As cannabis policy reform continues to sweep the globe, Ireland has launched a medical cannabis pilot program,...
What Technology Will Most Impact The Cannabis Industry? 24 Experts Share Their Insights
Disruptor Daily Cannabis legalization is gaining serious steam, and the industry is coming to a crossroads as nationwide demand for...
Solaris Farms Tackles Desert Heat with Global Tech
CannabisTech When Michael Sassano founded Solaris Farms in the Las Vegas area in 2016, his goals were ambitious - create...
What Trends Are Shaping The Cannabis Industry In 2019? 25 Experts Weigh In
Disruptor Daily Considering the topic of this article, you'd be forgiven for wondering whether it's 4/20 yet. It's not, but...
What’s The Future Of The Cannabis Industry? 28 Experts Share Their Perspectives
Disruptor Daily Bob Dylan once said that the times are a-changin', and no industry echoes that message like the cannabis...
CANNABIS INTERVIEW – MICHAEL SASSANO – FOUNDER SOLARIS FARMS
Cannabis Magazine Want to know more about one of the world’s largest greenhouses for growing cannabis? We sat down with...
Mike Sassano – A Cannabis Business in the Opportunity Zone
BuzzSprouts Mike Sassano's eclectic career has taken him from Cleveland to Wall Street, to Monaco and now Las Vegas. As...
Define “Organic”: The Cannabis Movement Is Stuck On Labeling
Dope Magazine Michael Sassano of Nevada’s Green Cross of America said all cannabis grown in the state is done without...